Figure 3.
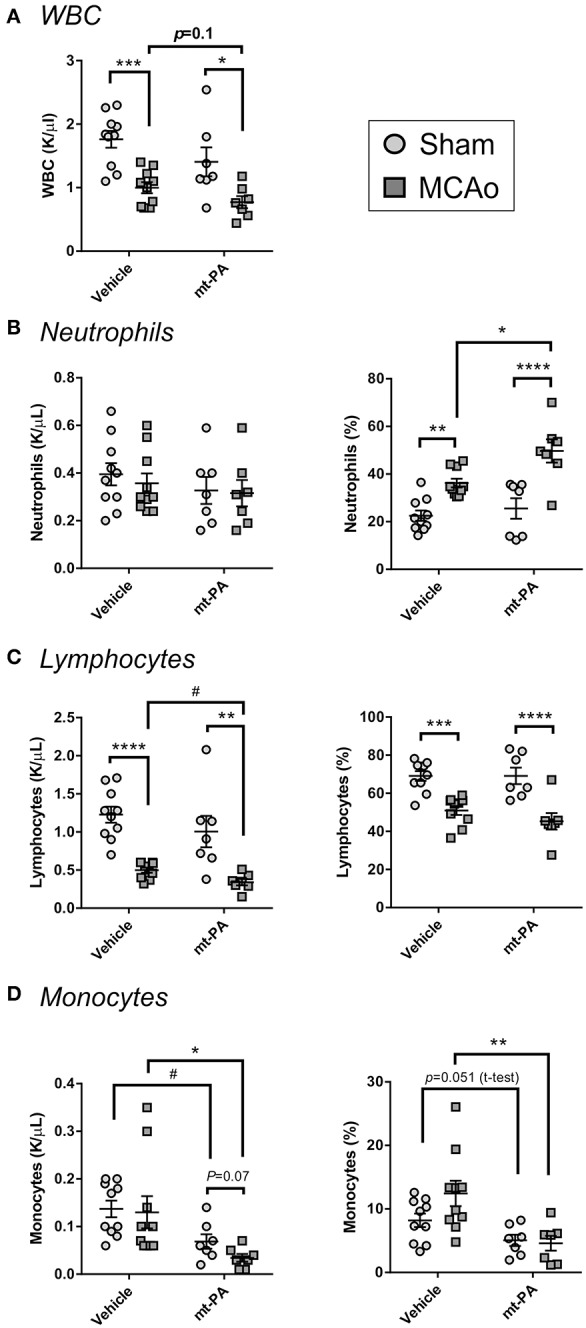
t-PA exacerbates stroke-triggered changes in blood leukocyte counts and proportions. Hemavet blood counts (left panels) and proportions (right panels) of total white blood cells (WBC; A), neutrophils (B), lymphocytes (C), and monocytes (D) 23 h after administration at reperfusion of HEPES vehicle or mouse t-PA (mt-PA; 0.9 mg/kg) to C57Bl/6 mice undergoing sham surgery or transient MCAo (1 h). Stroke causes robust leukopenia (A) and lypmhopenia (C), which are exacerbated by treatment with t-PA. t-PA also causes significant monocytopenia in both sham and MCAo mice compared to vehicle (D). Neutrophil proportion in blood is significantly elevated after stroke and further increases by t-PA, but neutrophil numbers remain unchanged (B). These observations indicate potentiation of stroke effects on blood leukocytes by t-PA. Data is shown as individual animals with mean ± SEM. n = 10 for sham vehicle, 7 for sham mt-PA, 10 for MCAo vehicle, 7 for MCAo mt-PA. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 by two-ANOVA with Sidak's post-hoc, #p < 0.05 by the student t-test.
