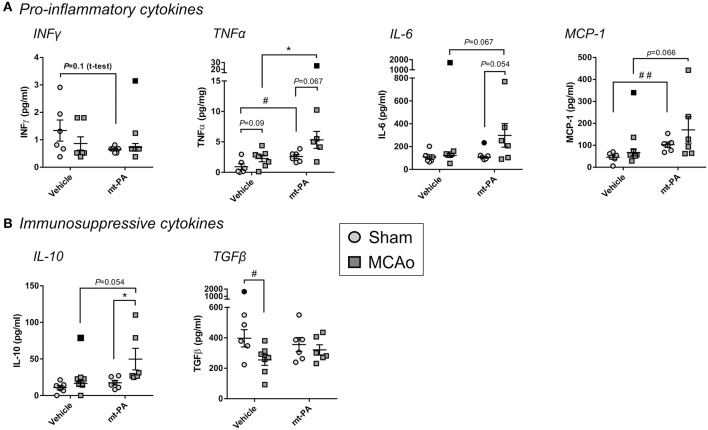
Figure 4.
Plasma cytokine levels after stroke are affected by t-PA treatment. Pro-inflammatory (A) and immunosuppressive (B) cytokine levels measured by multiplex ELISA in mouse plasma 23 h after administration at reperfusion of HEPES vehicle or mouse t-PA (mt-PA; 0.9 mg/kg) to C57Bl/6 mice undergoing sham surgery or transient MCAo (1 h). t-PA treatment significantly elevates pro-inflammatory and immunosuppressive cytokines in shams as well as in MCAo mice compared to vehicle, most notably TNFα, MCP-1 (A) and IL-10 (B), respectively. Trends for reduction of INFγ (A), elevation of IL-6 (A) and reversal of stroke-induced TGFβ suppression (B) are further observed in t-PA-treated mice. This cytokine profile demonstrates pleotropic effects of t-PA on immune function, which at least in part could contribute to immunosuppression after stroke. Data is shown as individual animals with mean ± SEM. n = 6 for sham vehicle, 6 for sham mt-PA, 7 for MCAo vehicle, 6 for MCAo mt-PA. *p < 0.05 by two-ANOVA with Sidak's post-hoc, #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 by the student t-test. Outliers are denoted in black symbols and excluded from the analysis.