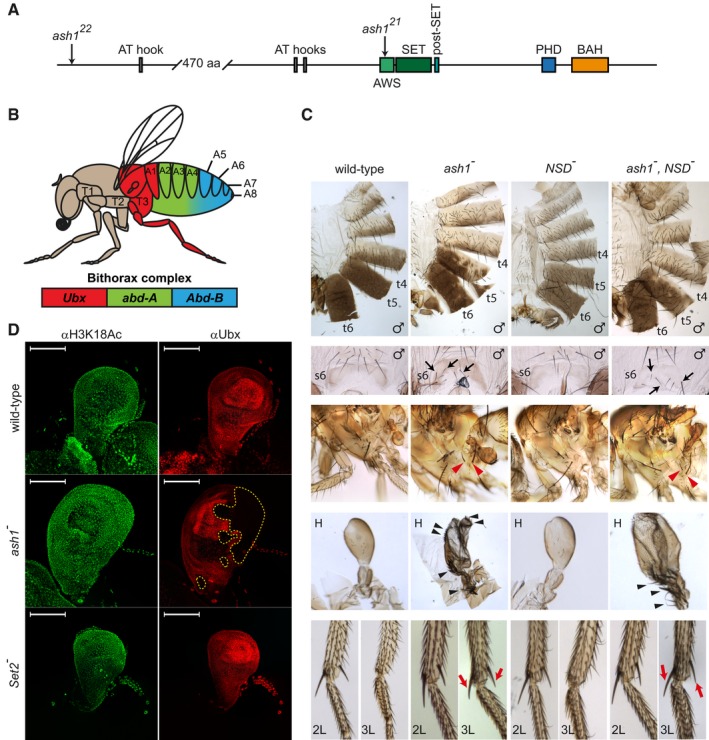
The schematic of the Drosophila Ash1 protein organization. Ash1 is 2,226 amino acid long and contains eight domains (indicated by coloured rectangles). The SET domain together with the AWS (Associated With SET) and the post‐SET domains are necessary and sufficient for Ash1 histone methyltransferase (HMTase) activity. The functions of the BAH (Bromo Adjacent Homology), PHD (Plant homeodomain) and AT‐hook domains are unknown. The positions of ash1
22 and ash1
21 point mutations are indicated by arrows.
Segmental expression of the Drosophila bithorax complex genes. The three genes of the complex, Ubx, abd‐A and Abd‐B, are shown as coloured rectangles. The expression of Ubx gives identity to the third thoracic (T3) and the first abdominal (A1) segments, the expression of abd‐A defines the second, third and fourth abdominal segments (A2–A4), and the expression of Abd‐B gives identity to the rest of the abdominal segments (illustrated with corresponding colour code).
Adult phenotypes of the ash1 and NSD mutants. In ash1
22/ash1
21 mutants (designated as ash1
−), the loss of Abd‐B expression results in partial transformation of abdominal segments 6 and 5 towards segments 5 and 4, which is visible from the partial loss of pigmentation on tergites 5 and 6 (t5 and t6) and appearance of bristles on sternite 6 (s6, marked with black arrows). The loss of Ubx expression causes transformation of the third thoracic to the second thoracic segment visible as partial haltere (H) to wing and third leg (3L) to second leg (2L) transformations. The former is evident from the change in the haltere shape and the appearance of multiple bristles (black arrowheads). The latter is indicated by the apical and pre‐apical bristles (red arrows) on the tibia of the third leg of ash1 mutants. These are normally present on 2L but absent on 3L (compare to wild‐type). Also note the appearance of additional hypopleural bristles on the third thoracic segment of the ash1
− flies (red arrowheads), which indicate its transformation towards the second thoracic segment. Phenotype of the NSD
ds46/NSD
ds46 (NSD
−) flies is indistinguishable from wild‐type and the phenotype of the double ash1
22
,NSD
ds46/ash1
22
,NSD
ds46 (ash1
−
,NSD
−) flies is no more severe than that of the single ash1
22/ash1
21 (ash1
−) mutants.
Ubx expression in the haltere imaginal discs. The expression was assayed by immunostaining with antibodies against Ubx (red) and acetylated H3K18 (green, positive control). While ash1
22/ash1
21 (ash1
−) larvae show stochastic clonal loss of the Ubx immunostaining in haltere discs (yellow dashed lines), Set2
− larvae have uniform expression of Ubx throughout the haltere disc, resembling that in the wild‐type larvae. Scale bars indicate 100 μm.