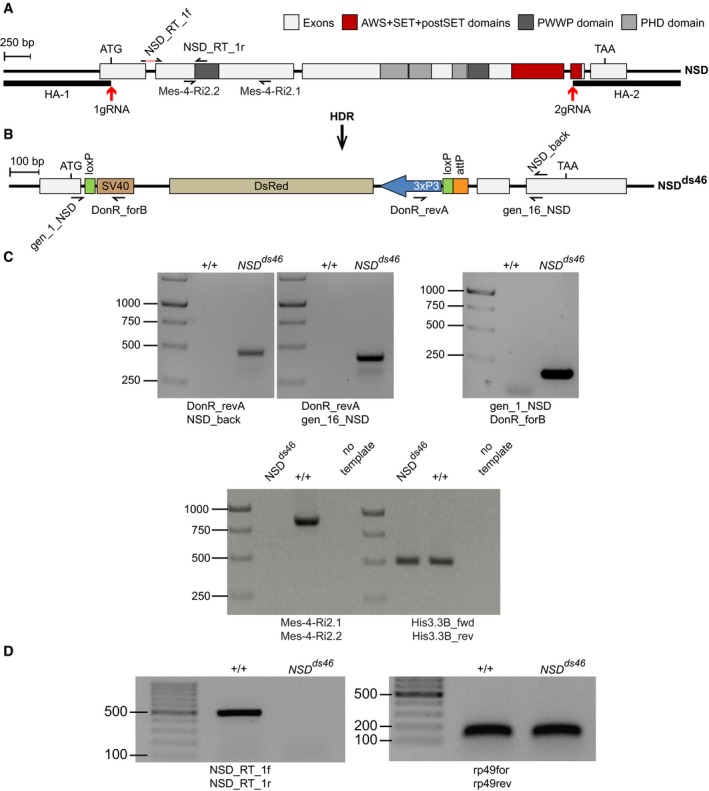
The structure of the Drosophila NSD locus. Red arrows indicate locations of the gRNA sites used for CRISPR/Cas9‐mediated replacement of the NSD Open Reading Frame (ORF) with DsRed. The homology regions HA‐1 and HA‐2, used for the replacement, are shown with bold lines. The half‐arrows represent the primers used for genotyping of the mutant allele. The dashed red line in NSD_RT_1f primer, used for RT–qPCR, indicates the intronic region that is excluded from the primer.
The NSD
ds46 allele. After Homology‐directed Repair (HDR), the insertion of the DsRed cassette generates the loss‐of‐function allele NSD
ds46, where DsRed substitutes most of the NSD ORF. The DsRed expression is controlled by the 3xP3 promoter. In addition to DsRed, the replacement cassette contains two loxP sites to remove DsRed via Cre‐mediated recombination and an attP docking site to insert variants of the NSD ORF. The half‐arrows represent the primers used to genotype the mutant allele.
Genotyping of the NSD
ds46 allele by PCR. The replacement of the NSD ORF by the DsRed cassette was confirmed by PCR with four different primers pairs. Three primer pairs (top row of images) yield the product only if the replacement has happened. The expected sizes of the PCR products are 469, 427 and 186 bp for DonR_revA and NSD_back, DonR_revA and gen_16_NSD, and gene_1_NSD and DonR_forB primer pairs, respectively. The PCR with Mes‐4‐RI‐2.1 and Mes‐4‐RI‐2.2 primer pair amplifies the 830 bp product only from the wild‐type allele. PCR with His3.3B_fwd and His3.3B_rev primer pair, amplifying the 495 bp DNA fragment from the His3.3B gene, was used as a positive control.
The NSD
ds46 allele produces no messenger RNA. This was confirmed by RT–PCR with NSD_Rt_1f and NSD_Rt_1r primer pair, which yields the 513 bp product only when the intact NSD mRNA is produced. RT–PCR with rp49for and rp49rev primer pair that amplifies 132 bp fragment from the cDNA of constitutively expressed RpL32 (a.k.a rp49) gene was used as positive control.