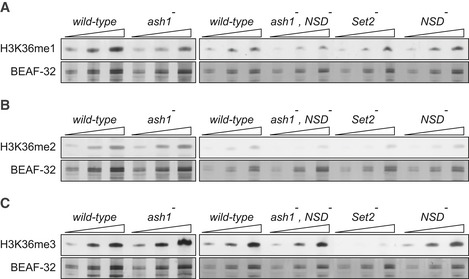
Figure 3. Western blot analysis of the bulk H3K36 methylation in larval tissues of various mutants.
-
A–CTwofold serial dilutions of the total protein extracts from the wild‐type, ash1 22/ash1 9011 (ash1 −), ash1 22 ,NSD ds46/ash1 9011 ,NSD ds46 (ash1 − , NSD −) and Set2 1 (Set2 −) larval brains, imaginal discs and salivary glands were analysed by Western blot with antibodies against H3K36me1 (A), H3K36me2 (B) and H3K36me3 (C). Note the strong (> 10‐fold) reduction of H3K36me3 signal in the Set2 − extract and the slight (˜ 2‐fold) reduction of H3K36me1 signal in the ash1 − and ash1 − , NSD − extracts. The protein extracts from the wild‐type, double ash1 − , NSD − and single NSD − and Set2 − mutants (right panels) were analysed together on the same membrane; however, the images of the H3K36me1 and H3K36me3 Western blots were modified to splice out the marker lane between the ash1 − , NSD − and the Set2 − extracts. Western blots with constitutively expressed BEAF‐32 protein were used as loading controls.
Source data are available online for this figure.
