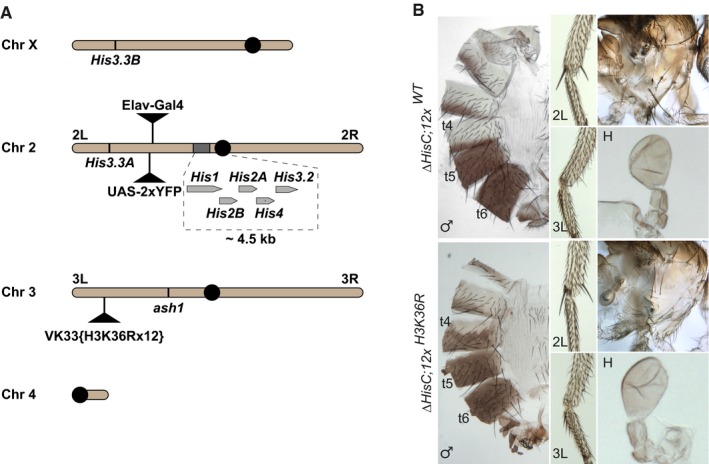
Chromosomal positions of various histone H3 genes,
ash1 and marker transgenes. Twenty‐three histone gene repeat units, each containing single
His1,
His2B,
His2A,
His4 and
His3.2 gene, are clustered near the centromere (black circle) of chromosome 2. These histone genes are removed by the
ΔHisC deletion. To select the animals homozygous for the deletion, the
ΔHisC chromosomes are marked with insertions of either
Elav‐Gal4 or
UAS‐2xYFP transgenes (black triangles on chromosome 2L). The
His3.3A and
His3.3B genes encode the same protein, but reside on chromosomes 2L and X. The transgenes carrying twelve copies of either the wild‐type histone repeat unit (
12x
WT) or the unit in which
H3 gene is altered to have K36 replaced with arginine (
12x
H3K36R) are inserted in the same
attP site (black triangle on chromosome 3L)
47. The
ash1 gene is located on the same chromosome arm.