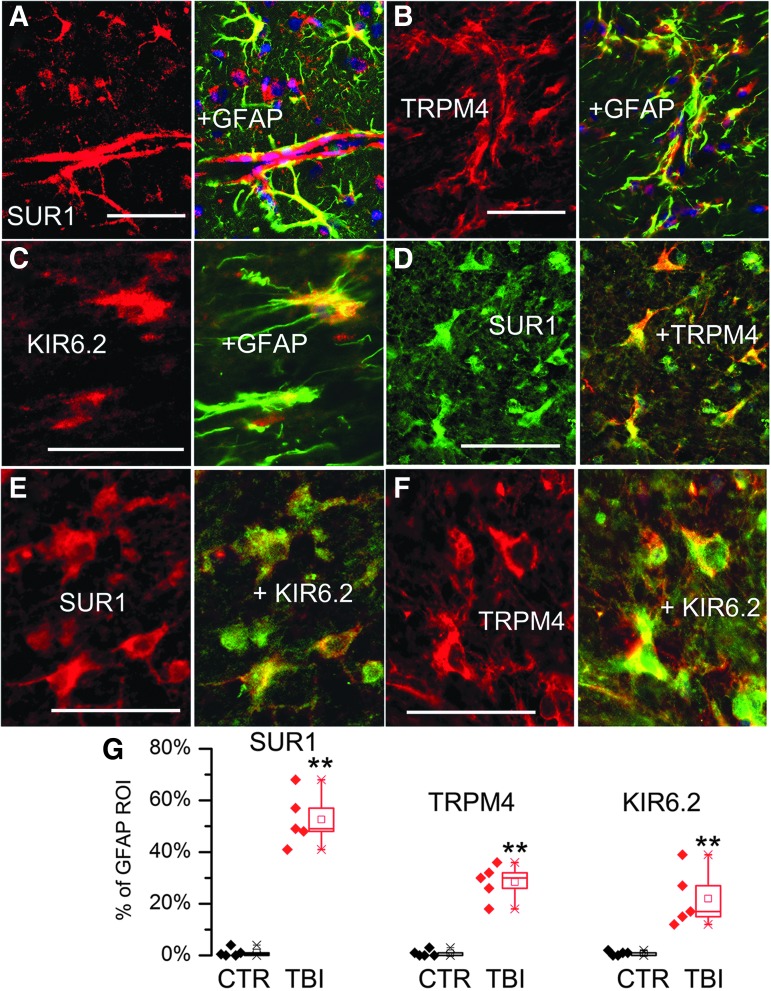
FIG. 9.
Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)–positive specimens from rat contusion– traumatic brain injury (TBI) exhibit sulfonylurea receptor 1 (SUR1) expression in astrocytes. (A-C) Double immunolabeling for GFAP (green) and SUR1 (A) or transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 4 (TRPM4) (B) or KIR6.2 (C) showed expression of all three channel subunits in astrocytes; merged images are shown in the right panels (yellow). (D-F) Double immunolabeling for SUR1 and TRPM4 (D), SUR1 and KIR6.2 (E), and TRPM4 and KIR6.2 (F), shows co-localization in astrocytes; merged images are shown in the right panels (yellow). (G) Expression of SUR1, TRPM4 and KIR6.2 in GFAP-positive astrocytes in TBI specimens (red) vs. controls (black); quantification performed based on GFAP-defined region of interest; scatterplots as well as box plots are shown; box plot symbols are the same as in Figure 4: Note that in controls, GFAP-positive astrocytes expressed minimal channel subunits, whereas all three channel subunits were expressed in GFAP-positive astrocytes in contusion-TBI specimens; **p < 0.01.