Figure 10.
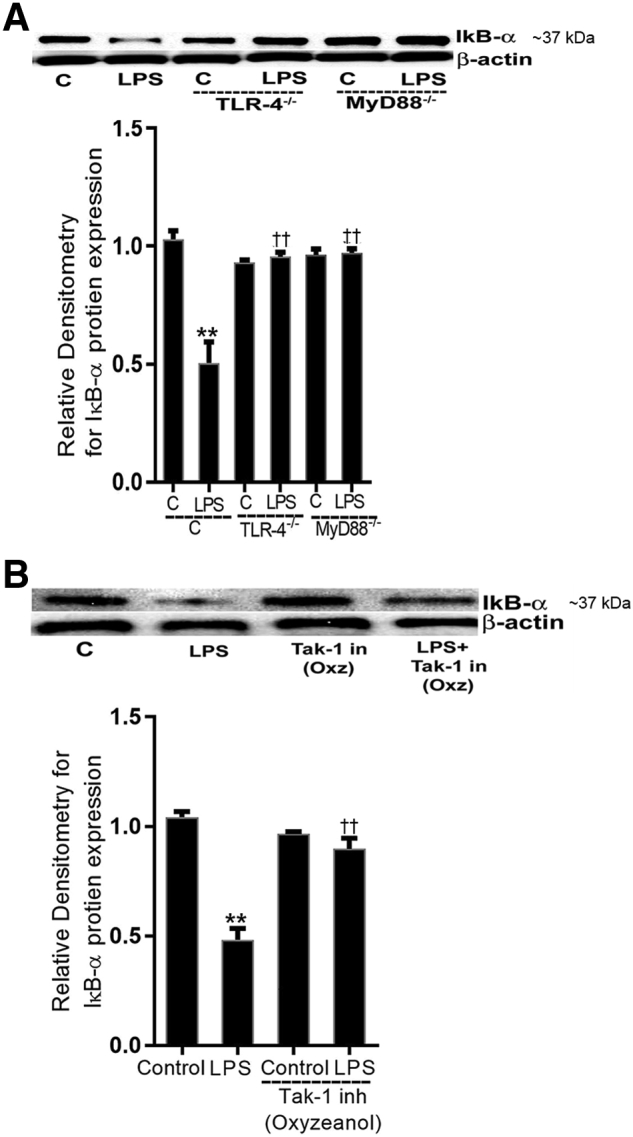
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced activation of NF-κB canonical pathway was inhibited in toll-like receptor (TLR)-4−/− and myeloid differentiation primary response (MyD)88−/− mice and with transforming growth factor-β–activating kinase (TAK)-1 inhibition. A: LPS i.p. injections (0.1 mg/kg body weight) in TLR-4−/− and MyD88−/− mice did not induce inhibitory κ B (IκB)-α degradation (day 3) compared with TLR4+/+ and MyD88+/+ control (C) mice, respectively. Densitometry of IκB-α protein. B: Pretreatment with TAK-1 inhibitor (in; inh), oxyzeanol (Oxz; 5 mg/kg body weight), prevented the LPS-induced degradation of IκB-α expression (day 3) compared with vehicle- or LPS-treated mice. Densitometry of IκB-α protein levels. n = 3 experiments. ∗∗P < 0.01 versus control; ††P < 0.01 versus LPS.
