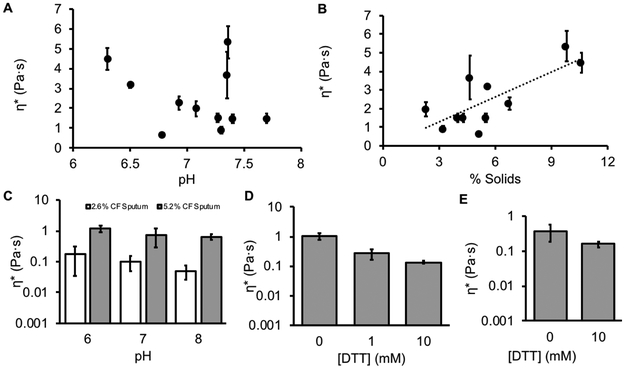
Figure 5:
CF sputum targets and candidate muco-corrective therapeutic strategies. A: Complex viscosity vs. % solids for CF sputum exhibited a significant relationship (n = 11, p = 0.006, r2 = 0.58). B: Complex viscosity (η*) vs. pH for CF sputum samples exhibited no significant correlation (p = 0.42). C: Complex viscosity of pooled, homogenized CF sputum at 5.2 (grey) and 2.6% (white) solids, pH 6, 7, and 8. Two-way ANOVA indicated that complex viscosity was correlated to concentration (p = 0.013), but not pH (p = 0.10). D: Reduction of normal HBE mucus by DTT. The reduction of mucus by 10 mM DTT was found to be significantly different than control (p = 0.027). E: Reduction of 5% pooled CF sputum shows a similar reduction when treated with 10mM DTT (p = 0.008). For reference, the viscosity of water is ~ 0.001 Pa·s.