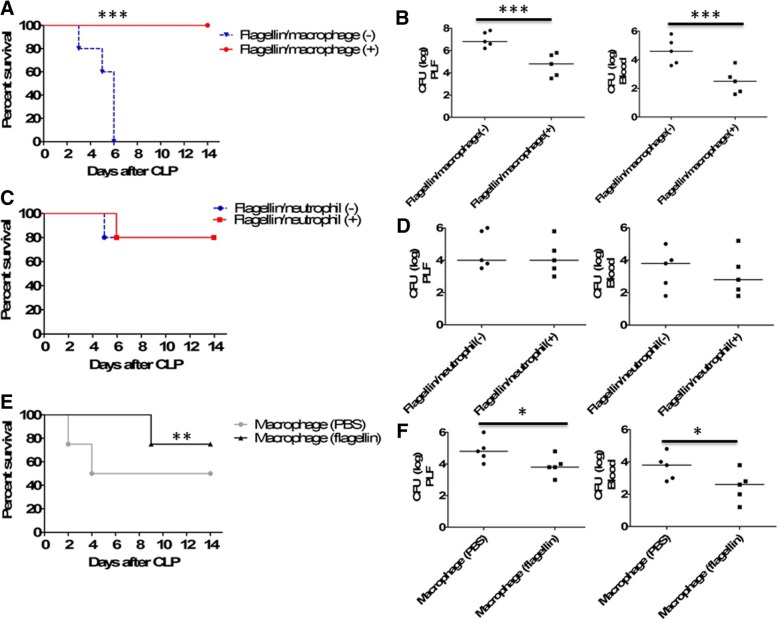
Fig. 3.
Macrophages were required for flagellin-mediated beneficial effects on cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)–induced sepsis. a Mortality after macrophage depletion by clodronate liposomes and subsequent treatment with flagellin (5 μg) or PBS control in mice (n = 20) after sublethal CLP using a 26-gauge needle. Comparison between groups was done by Kaplan–Meier analysis followed by log-rank tests. ***p < 0.001 when compared with wild-type mice treated with PBS liposomes as a control. b Bacterial counts in PLF and blood from flagellin-treated mice (n = 5 per group) with or without macrophage depletion 24 h after CLP. ***p < 0.001when compared between groups (denoted by the horizontal bracket; Mann–Whitney U test). c Mortality after neutrophil depletion by anti-RB6-8C5 monoclonal antibodies and subsequent treatment with flagellin (5 μg) or PBS control in mice (n = 20) after CLP. d Bacterial counts in PLF and blood from flagellin-treated mice (n = 5 per group) with or without neutrophil depletion 24 h after CLP. e Survival after transfer of flagellin-treated macrophages in mice (n = 20) with CLP-induced sepsis. Comparison between groups was done by Kaplan–Meier analysis followed by log-rank tests. **p < 0.01 when compared with mice treated with PBS-treated macrophages. f Bacterial counts in PLF and blood from mice (n = 5) transferred with flagellin-treated or PBS-treated macrophages. *p < 0.05 when compared between groups (denoted by the horizontal bracket; Mann–Whitney U test)