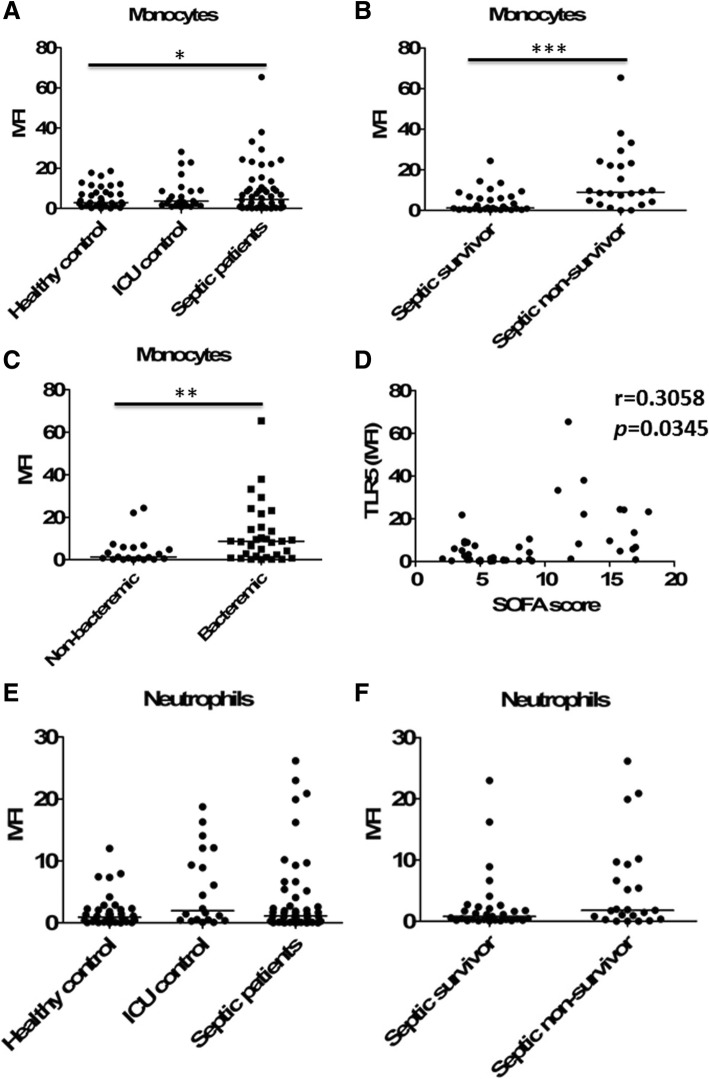
Fig. 7.
Increased expression of TLR5 on circulating monocytes was related to poorer outcomes of septic patients. a The expression of TLR5 on the surface of peripheral blood monocytes from the studied subjects. n = 37 for healthy controls, n = 23 for ICU controls, and n = 53 for sepsis patients. The expression of TLR5 was shown as MFI subtracting corresponding isotypic controls and with scatter plots showing the median. *p < 0.05 when compared between groups (denoted by the horizontal bracket; Mann–Whitney U test). b The expression of TLR5 on the surface of peripheral blood monocytes from the septic survivors (n = 30) and the septic non-survivors (n = 23). Horizontal bars represent median values, and dots represent individual participants. ***p < 0.001 when compared between groups (denoted by the horizontal bracket; Mann–Whitney U test). c The expression of TLR5 on the surface of peripheral blood monocytes from the septic patients with (n = 33) or without (n = 20) documented bacteremia. **p < 0.01 when compared between groups (denoted by the horizontal bracket; Mann–Whitney U test). d Correlation of TLR5 expression levels on the surface of peripheral blood monocytes with Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) scores in the septic patients (Spearman’s rank correlation test). e The expression of TLR5 on the surface of peripheral blood neutrophils from the studied subjects. f The expression of TLR5 on the surface of peripheral blood monocytes from the septic survivors (n = 30) and the septic non-survivors (n = 23)