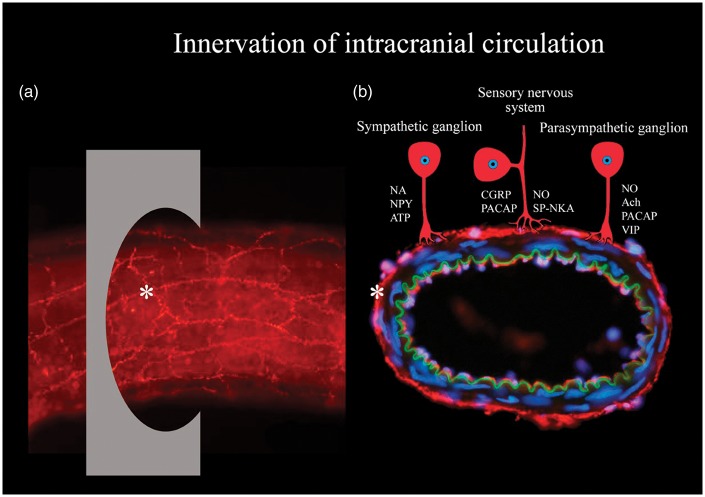
Figure 1.
Overview of innervation of intracranial vasculature. (a) Whole-mounted intracranial vessel immunohistochemically processed using anti-transmitter antibodies. Asterisk point at transmitter innervation of a nerve, and also at the region of perpendicular section shown in Figure 3(b). (b) An intracranial vessel (from the inside and out): endothelium (red), lamina elastic interna (green), unstained smooth muscle cells, transmitter immunoreactive nerves (red) and nuclei (blue). Transmitter innervation is displayed by schematic drawings of neurons. Abbreviations: Ach: acetylcholine; ATP: adenosine triphosphate; CGRP: calcitonin gene-related peptide; NA: noradrenaline; NKA: neurokinin A; NO: nitric oxide; NPY: neuropeptide Y; PACAP: pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide; SP: substance P; VIP: vasoactive intestinal peptide.