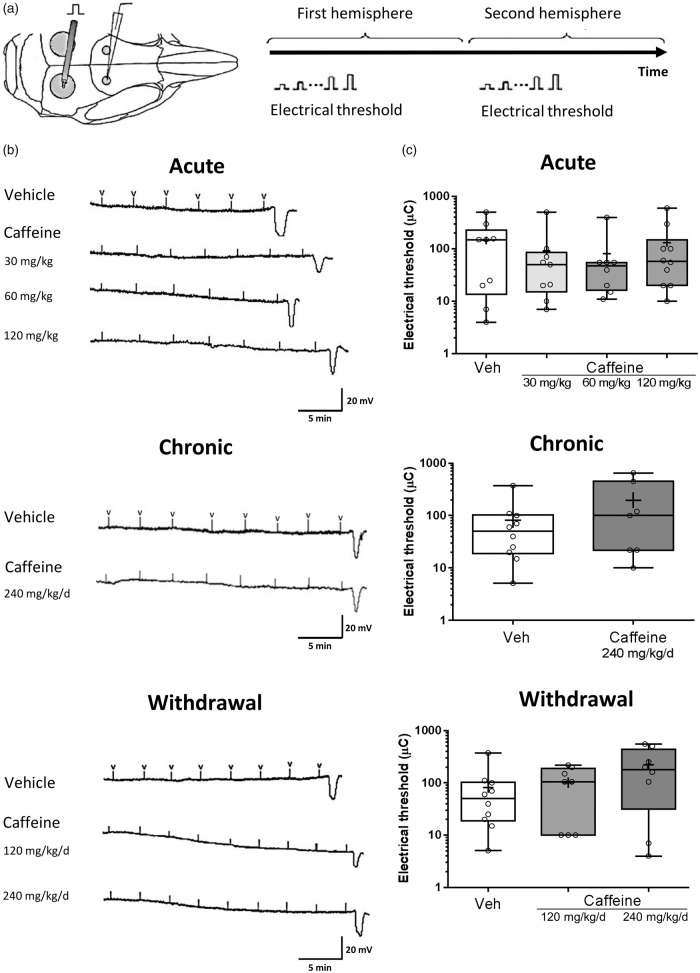
Figure 1.
Caffeine does not affect the electrical threshold for cortical spreading depolarization in mice.(a) Single-squared pulses of increasing duration and intensity (2–900 µC) were applied at 3-min intervals, until a CSD was observed. The two hemispheres were studied consecutively to investigate a possible effect of pharmacokinetic changes of caffeine on CSD along the time course after administration. (b) Representative tracings of electrical threshold for CSD in each group, with “V” indicating electrical stimulus administration. (c) Whisker box plots show that acute (0 mg/kg n = 9; 30 mg/kg n = 9; 60 mg/kg n = 9; 120 mg/kg n = 10) or chronic (0 mg/kg/day n = 10 (1 week); 240 mg/kg/day n = 7 (1 week)) caffeine administration did not affect the electrical threshold for CSD. Similarly, caffeine withdrawal (0 mg/kg n = 10; 120 mg/kg/day n = 8 (1 week); 240 mg/kg/day n = 8 (1 week)) had no effect on CSD threshold in C57BL/6 J mice (p > 0.05). The ends of the whiskers represent minimal and maximal data points. The horizontal lines within the box indicate the median, and the “+” sign represents the mean. Open circles show individual data points.