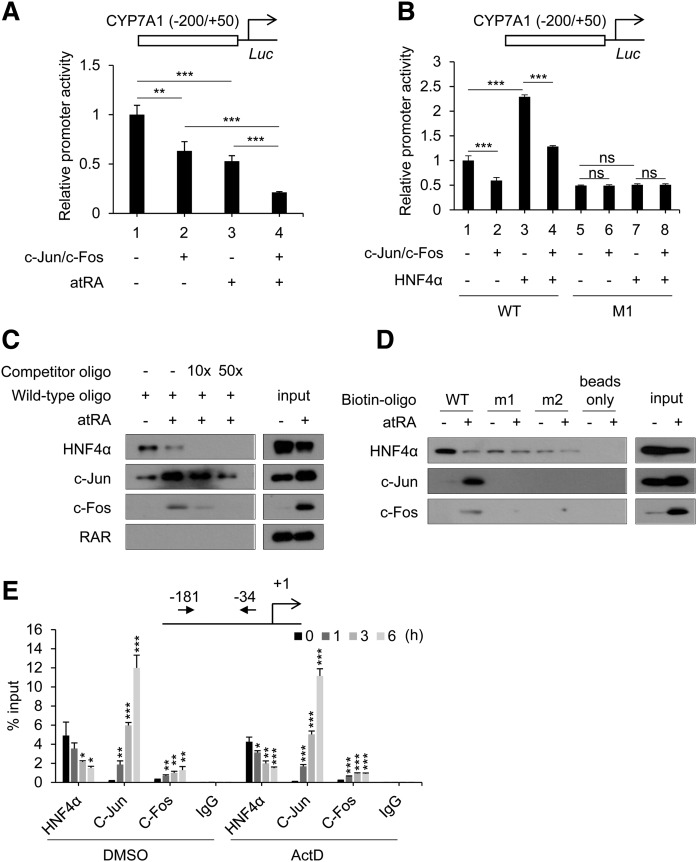
Fig. 5.
AP-1 proteins are recruited to the HNF4α-binding site of the CYP7A1 promoter in a HNF4α-dependent manner. A: HepG2 cells were cotransfected with CYP7A1 promoter luciferase vector and expression vectors (c-Jun and c-Fos) and treated with atRA (1 µM) for 24 h, and promoter activity was measured (n = 3, mean ± SD). * P < 0.05; *** P < 0.001. B: HepG2 cells were cotransfected with CYP7A1 promoter luciferase vector and HNF4α expression vectors, and promoter activity was measured (n = 3, mean ± SD). *** P < 0.001; ns, not significant. M1, mutated HNF4 binding site. C, D: HepaRG cells were treated with atRA (1 µM) for 3 h. Western blot analysis was performed after DNA pull-down using the biotinylated oligonucleotides indicated and nuclear extracts. E: HepaRG cells were pretreated with Actinomycin D (ActD; 2 µg/ml) for 1 h and treated with atRA (1 µM) for the time periods indicated, and ChIP assay was performed (n = 3, mean ± SD). * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001 versus control (0 h).