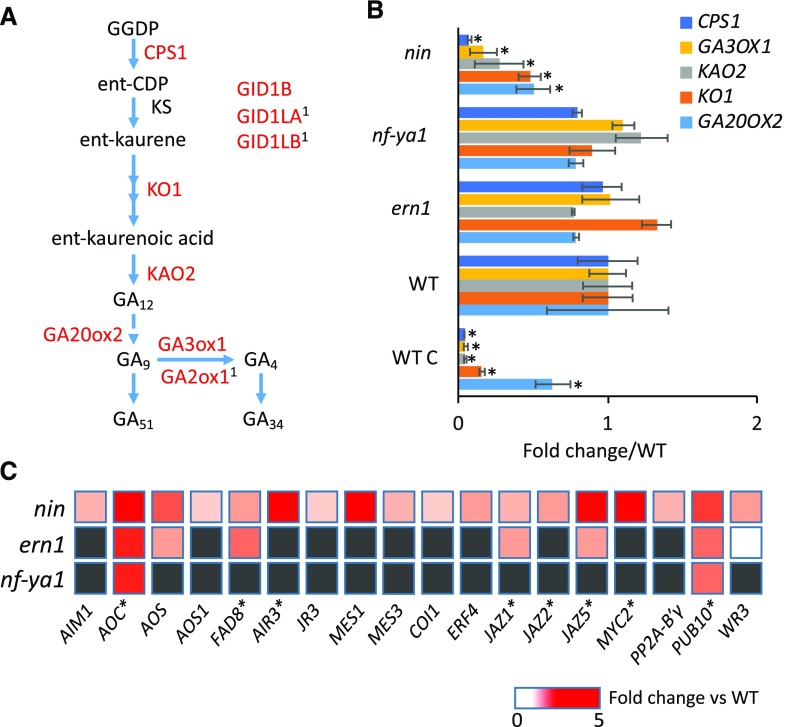
Figure 5.
Genes for GA and JA biosynthesis and signaling have decreased and increased expression, respectively, in root hairs of nin after rhizobial inoculation. A, The GA biosynthetic pathway in plants. CPS1, ENT-COPALYL DIPHOSPHATE SYNTHETASE1; KS, KAURENE SYNTHASE; KO1, ENT-KAURENE OXIDASE1; KAO2, ENT-KAURENOIC ACID HYDROXYLASE2; GA20ox2, GIBBERELLIN 20-OXIDASE2; GA3ox1, GIBBERELLIN 3-OXIDASE1; GA2ox1, GIBBERELLIN 2-OXIDASE1; GID1B, GA INSENSITIVE DWARF1B; GID1LA/B, GID1-LIKEA/B. Genes encoding the enzymes in red are significantly down-regulated in nin. Superscript 1 indicates that the gene was identified using NIN ChIP-seq by Soyano et al. (2014). B, Expression of GA biosynthesis genes in root hairs of ern1, nin, and nf-ya1 mutants relative to the wild type (WT; A17) at 5 dpi with S. meliloti Rm1021. Bars indicate 95% confidence interval. *, P ≤ 0.05, Student’s t test; mutants are compared with the wild type, and the wild type is compared with its control (WT C), which was inoculated with S. meliloti Rm1021 ΔnodD1ABC. C, Expression of JA-related genes in root hairs of nin, nf-ya1, and ern1 mutants relative to the wild type (A17) at 5 dpi with S. meliloti Rm1021. Genes reported to be induced by methyl jasmonate are indicated by asterisks (Naoumkina et al., 2007). Only genes with mean expression significantly different from that of the wild type are indicated (gray boxes indicate that expression was not significantly different).