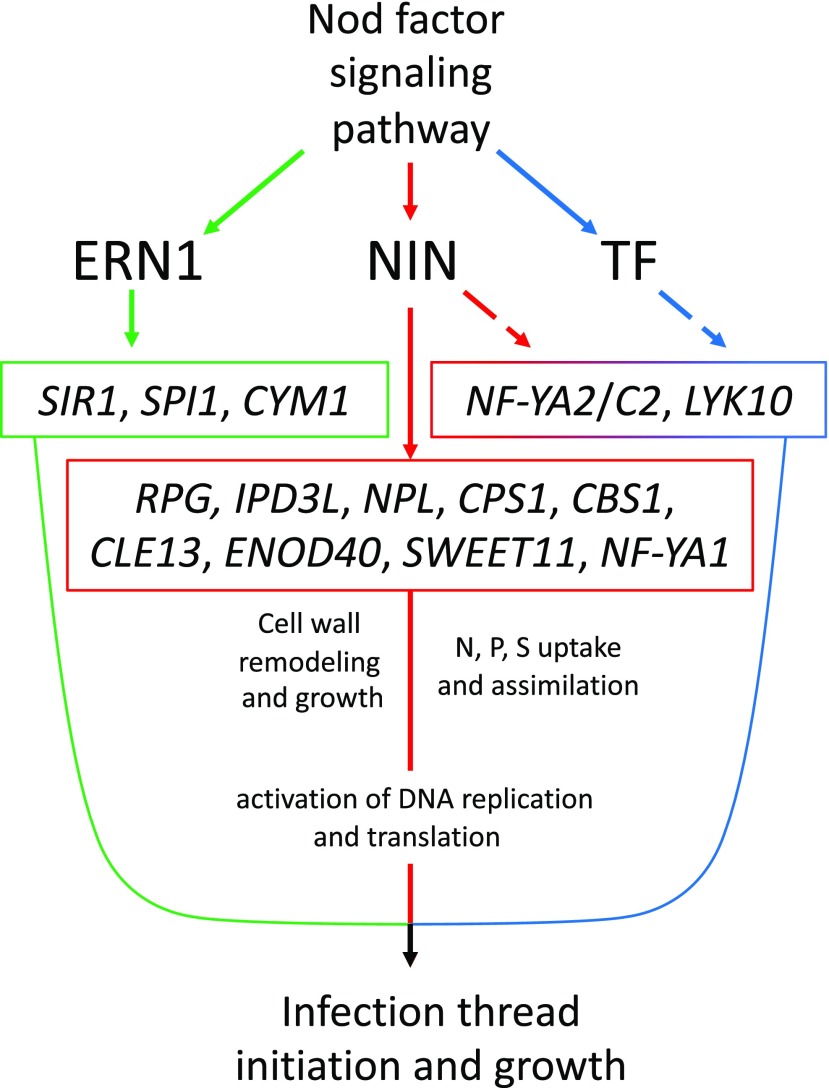
Figure 6.
Model for the gene regulatory network underlying rhizobial infection. Nod factor signaling induces the expression of NIN (red), ERN1 (green), and other transcription factors (TF; blue). ERN1 is required for up-regulation of a few genes with symbiotic specific expression, while NIN controls a diversity of functions, including cell wall modification via NPL, GA biosynthesis by genes like CPS1, and nutrient uptake and DNA synthesis either directly or through subordinate transcription factors such as NF-YA1/A2 and NF-YC2, components of the CCAAT-box transcription factor complex. Other genes, like RPG, require NIN for their expression during infection, but their exact roles in the symbiosis are unknown. Many genes are partly dependent on NIN but require another unidentified transcription factor or factors for their full expression during infection (broken lines).