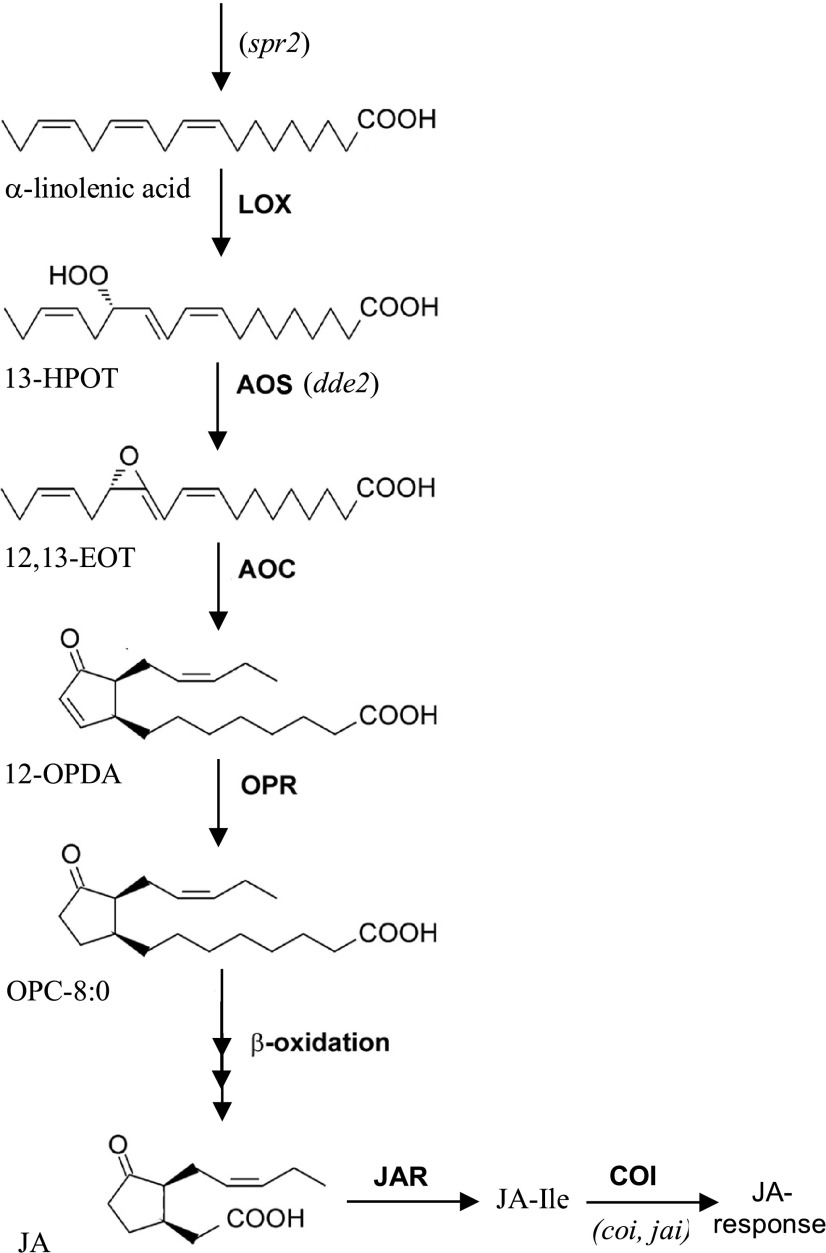
Figure 2.
Overview of JA biosynthesis pathway and related mutants. Only the main pathway of oxylipin synthesis to jasmonate is shown. Several branches occur that give rise to many other metabolites. In addition, several enzymes are encoded by multiple genes from a gene family, although only one is shown. Intermediates and derivates: 13-HPOT, 13-hydroperoxy-octadecatrienoic acid; 12,13-EOT, 12,13-epoxy octadecatrienoic acid; OPC-8:0, 3-oxo-2-(2-pentenyl)-cyclopentane-1-octanoic acid; JA-Ile, jasmonoyl-Ile. Enzymes: LOX, 13-lipoxygenase; OPR, 12-oxophytodienoate reductase; JAR, jasmonate response locus encoding a jasmonic acid-amido synthetase that converts JA into the bio-active JA-Ile. Mutants: spr2, suppressor of prosystemin response 2 mutant; coi1, the mutant in COI F-box protein involved in jasmonate signaling; jai, jasmonate insensitive, also mutant in COI.