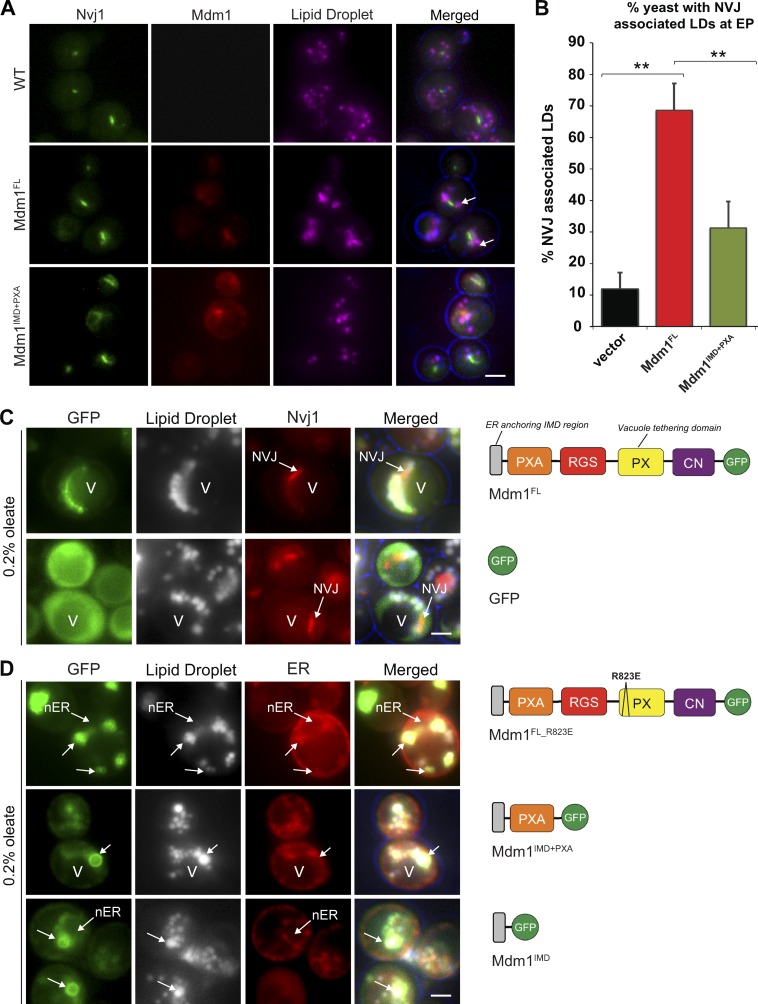
Figure 1.
Mdm1 binds LDs via its N-terminal hydrophobic motif. (A) Light microscopy of yeast expressing chromosomally tagged Nvj1-GFP (green) and expressing either mCherry-tagged Mdm1FL or Mdm1IMD+PXA (red). LDs (magenta) visualized by MDH staining (arrows). Scale bar, 2 µm. (B) Quantification of images in A. Percentage of yeast cells with NVJ-associated LDs over the total number of cells counted; mean ± SD; n > 50 cells; **, P < 0.005; Student’s t test. EP, exponential phase. (C) Light microscopy of yeast expressing GFP-tagged Mdm1FL or soluble GFP in yeast expressing chromosomally tagged Nvj1-mCherry in the presence of 0.2% oleate. LDs (gray) visualized by MDH staining. V, vacuole. Diagrams depict Mdm1 fragments expressed. Scale bar, 2 µm. (D) Light microscopy of yeast expressing different GFP-tagged Mdm1 fragments in yeast expressing chromosomally tagged ER marker Ds-Red HDEL in the presence of 0.2% oleate. LDs (gray) visualized by MDH staining. Diagrams depict Mdm1 fragments expressed. RGS: regulator of G protein signaling, CN: C-terminal Nexin. Scale bar, 2 µm.