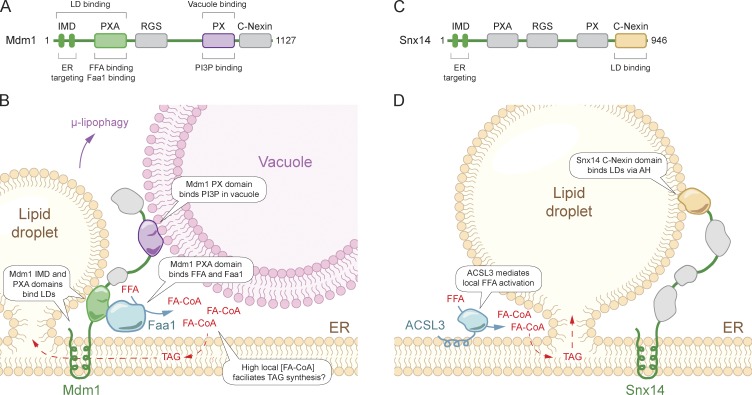
Figure 1.
Model of Mdm1 and Snx14 in the formation and regulation of LD MCSs. (A) Yeast Mdm1 domain structure. (B) Mdm1 functions as a tri-organelle tether, physically linking the ER, vacuole, and LDs. Mdm1 binds FFA and recruits Faa1, providing high local concentrations of activated FA that promote efficient neutral lipid synthesis and prevent lipotoxicity. (C) Human Snx14 domain structure. (D) Snx14 acts as an ER–LD tether and promotes LD biogenesis. AH, amphipathic helix.