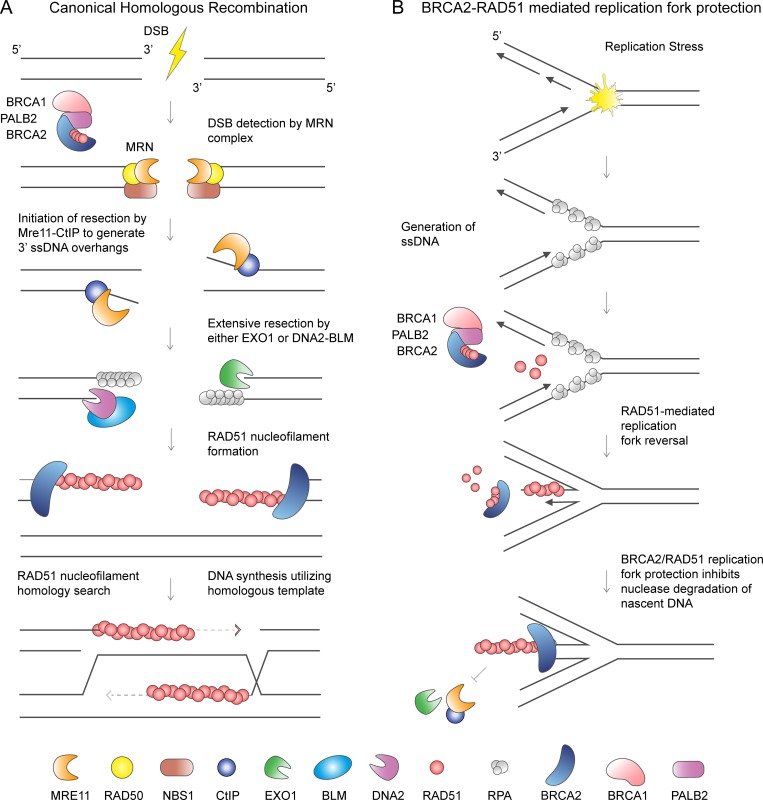
Figure 3.
Distinct roles of BRCA2 and RAD51 in canonical homologous recombination and replication fork protection. (A) HDR of DSBs requires the formation of 3′ ssDNA overhangs. The MRE11–RAD50–NBS1 (MRN) complex senses DSB and with the CtiP endonuclease initiates DNA end resection. The EXO1 exonuclease or the BLM–DNA2 helicase nuclease complex is responsible for more extensive resection. BRCA2 loads and stabilizes RAD51 nucleofilaments on the ssDNA overhangs displacing the ssDNA binding protein RPA. RAD51 nucleofilament invades the sister chromatid to perform homology search. DNA synthesis proceeds using homologous DNA for precise repair. (B) Replication fork reversal is proposed to be a global response to replication stress that requires RAD51 and BRCA2 for fork reversal and fork protection. RAD51-mediated fork reversal entails the annealing of the newly replicated (nascent) strands of DNA and reannealing of the parental DNA strands. This function is proposed to require RAD51 independently of BRCA2. Subsequently, both RAD51 and BRCA2 are necessary to prevent nascent strand degradation.