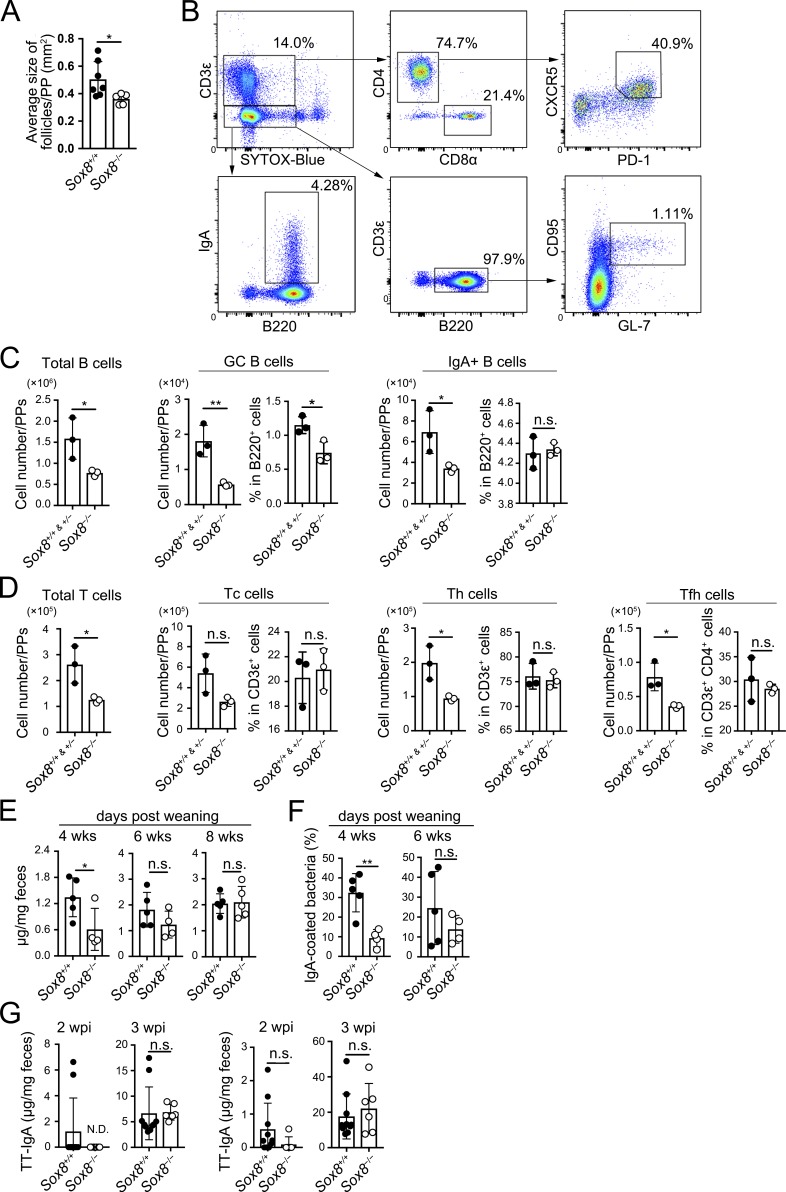
Figure 6.
The loss of Sox8 causes delay in the production of symbiotic bacteria-specific IgA antibody after weaning. (A) Follicle size of PPs measured by stereomicroscope; *, P < 0.05; Student’s t test; n = 7 from Sox8+/+ mice, n = 5 from Sox8−/− mice. (B) The gating strategy to analyze the B and T cell populations in ileal PPs. B (CD3ε−B220+) cells were analyzed for IgA+ B and CD95+GL7+ GC B cells. T (CD3ε+B220−) cells were analyzed for total CD4+ Th, CD8α+ cytotoxic T (Tc), and CD4+CD8α−CXCR5+PD-1+ Tfh cells. (C and D) Flow cytometry analysis of indicated immune cells in ileal PPs. (C) Number of total B cells, GC B cells, and IgA+ B cells. (D) Number of total T cells, Tc cells, Th cells, and Tfh cells; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; n.s., not significant; Student’s t test, n = 3 per group. (E) Fecal IgA concentration measured by ELISA; *, P < 0.05; Student’s t test; n = 5 from Sox8+/+ mice, n = 4 from Sox8−/− mice (4 and 6 wk old); n = 5 per group (8 wk old). (F) Flow cytometry analysis of IgA-coated bacteria in feces; **, P < 0.01; Student’s t test; n = 5 from Sox8+/+ mice, n = 4 from Sox8−/− mice. (G) Mice were orally infected with 5 × 107 CFU of rSalmonella-ToxC. The presence of TT-specific IgA in feces and IgG in serum at 2 and 3 wk after immunization were evaluated by ELISA; Student’s t test; n = 10 from Sox8+/+ mice, n = 6 from Sox8−/− mice. Data are representative (B–F) or means (A and G) of two independent experiments. wpi, weeks post-immunization. All values are presented as the mean ± SD.