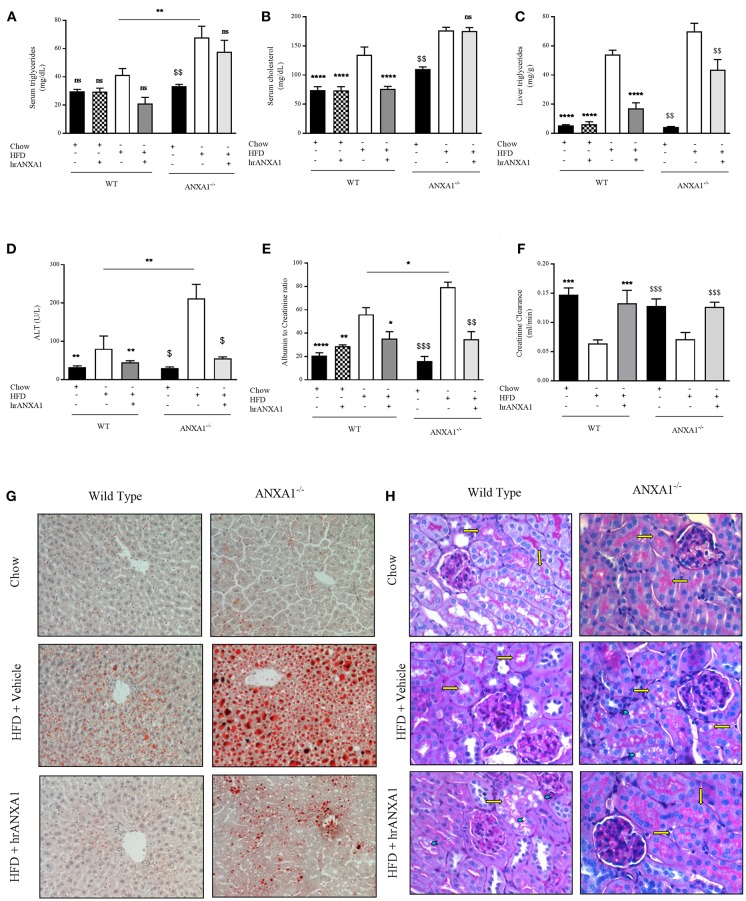
Figure 5.
ANXA1 attenuates induced lipid accumulation, hepatic injury, and renal dysfunction. C57BL/6 or ANXA1−/− mice, fed a standard diet (chow) or a HFD for 10 weeks, were treated with vehicle or human recombinant (hr) ANXA1 (40 μg/kg, i.p.) five times per week between weeks 5 and 10. Measure of (A) Serum triglyceride, (B) Serum cholesterol, (C) Liver triglyceride, (D) Serum aminotransferase (ALT), n = 6–8/group. (E) 18 h urine samples was collected and renal dysfunction was measured by albumin to creatinine ratio (ACR), n = 6–8 per group. (F) Creatinine clearance was measured from urinary and serum creatinine, n = 6–8 per group. (G): representative images of hepatic lipid deposition assessed by Oil Red-O staining. Panel (H): representative images of histological changes in kidney structure assessed by periodic acid-Schiff staining, yellow arrows indicating brush borders of proximal tubules. Data were analyzed by a one-way ANOVA followed by a Bonferroni post-hoc test and the mean is expressed mean ± SEM., *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 vs. WT + HFD. $p < 0.05, $$p < 0.01, $$$p < 0.001 vs. ANXA1−/− + HFD.