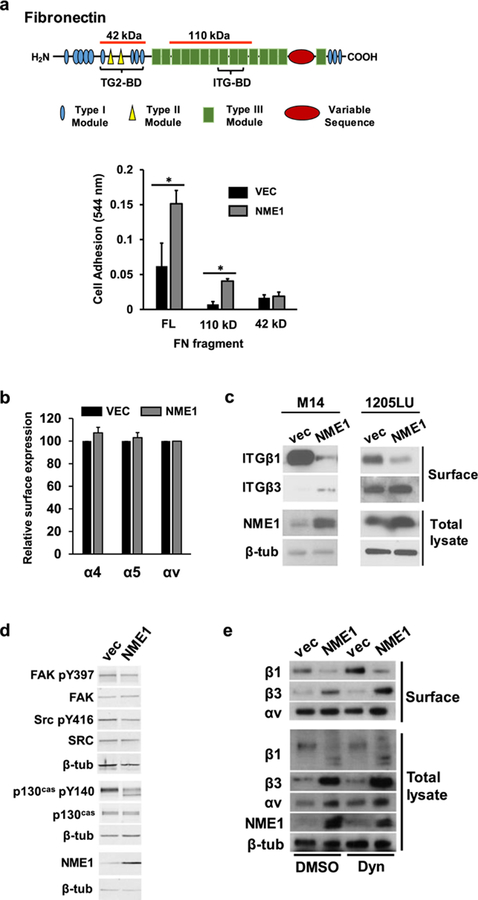
Figure 2.
NME1 promotes integrin-mediated adhesion to fibronectin (FN) via regulation of integrin beta subunit expression at the cell surface. (a) Adhesion assays were conducted as described 31, with minor modifications (Materials and Methods). Diagram depicts domains of the FN molecule; those associated with binding to integrins (ITG-BD) and transglutaminase 2 (TG2-BD) are indicated with brackets. Regions corresponding to FN fragments used in cell adhesion studies are identified with orange lines above the molecule (42 and 110 kDa, respectively). Bar graph summarizes adhesion of 1205Lu cells stably transfected with either empty or NME1 expression vector. Cells were incubated for 15 min on plates coated with full length (FL) fibronectin (FN) or FN fragments containing either the ITG-BD (110 kD) or TG2-BD (42 kD). *p≤0.05 by Student’s t-test. (b) Cell surface expression of the indicated alpha integrin subunits (α4, α5 and αv) was quantified in 1205Lu cells (−/+ forced NME1 expression) by flow cytometry. (c) NME1 expression induces a switch in cell surface expression from predominantly ITGβ1 to ITGβ3. Cell surface expression of beta integrins (“Surface”) was determined in the indicated M14- and 1205Lu-derived cell lines by surface biotinylation and immunoblot analysis, as described (Materials and Methods). Expression of NME1 and β-tubulin (β-tub) were measured in the “intracellular” compartment by immunoblot analysis. (d) Impact of forced NME1 expression on expression of total and activated forms of focal adhesion kinase (FAK), SRC and p130Cas was determined in M14 cells by immunoblot analysis. (e) Cell surface and intracellular expression of ITGβ1, ITGβ3 and ITGαv was measured in M14 cells (−/+ forced NME1 expression) following a 1h incubation with either vehicle (“DMSO”) or the dynamin inhibitor dynasore (“Dyn”; 80 mM).