Figure 1.
Characteristics of Meiocyte sRNA Clusters.
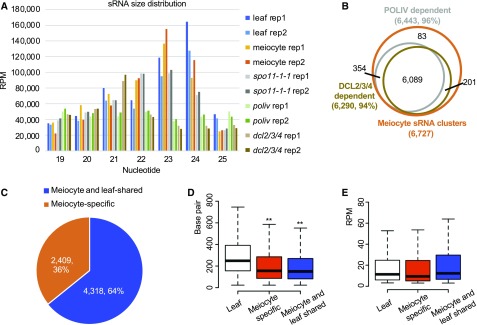
(A) Mappable sRNA size distribution from all samples examined. Each sample has two biological replicates. Adapters were trimmed from sRNA reads, and low quality reads and reads that mapped to ribosomal RNAs, transfer RNAs, small nRNAs, small nucleolar RNAs, miRNAs, and other annotated small nuclear RNAs were filtered out.
(B) The majority of meiocyte sRNAs are dependent on RNA Polymerase IV (POLIV) and DCL2/3/4.
(C) Thirty-six percent of sRNA clusters found in meiocytes are meiocyte-specific. ms-sRNA clusters are defined as the clusters having a <40% overlap rate or do not overlap with the sRNA clusters in leaves.
(D) Meiocyte sRNA clusters are significantly shorter than leaf sRNA clusters (**P value < 0.01). sRNA cluster length in leaves was compared with ms-sRNA cluster length and meiocyte/leaf-shared sRNA cluster length (both P value < 2.2e-16; Student’s t test).
(E) No significant difference in sRNA abundance was observed between leaf and meiocyte clusters. Student’s t test was used to compare RPM in leaf versus meiocyte-specific (P value = 0.35) and leaf versus meiocyte/leaf-shared (P value = 0.18).