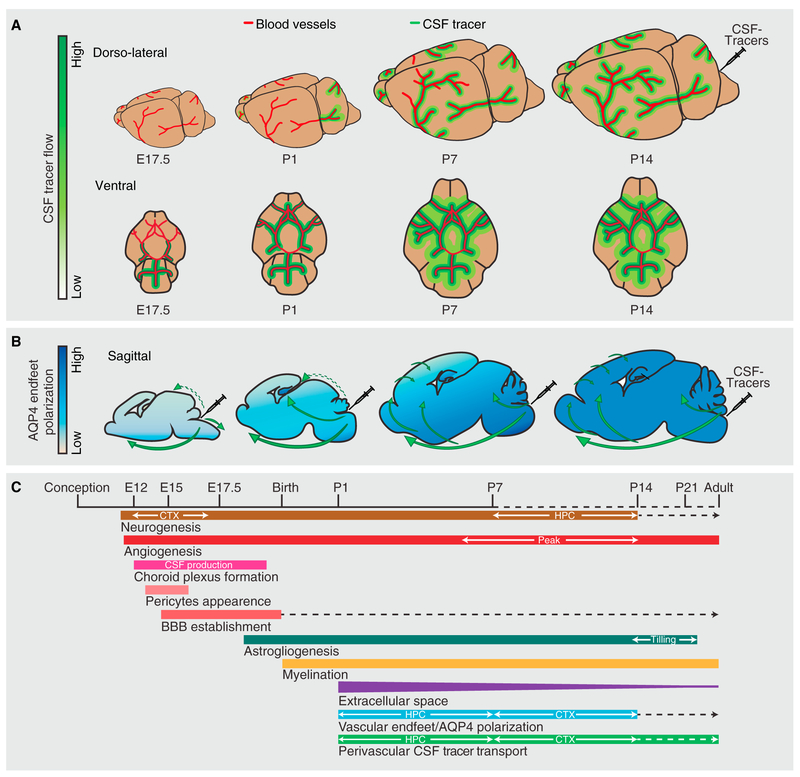
Figure 7. Glymphatic Flow Patterns during Development and Concurrent Developmental Events.
(A) Dorso-lateral view depicts the distribution patterns of CSF tracers in perivascular pathways of the MCA at mouse E17.5 and postnatal day (P) 1, P7, and P14. Ventral view shows the arterial circle of Willis and beginning of MCAs. Ventral perivascular flow along the circle of Willis is very faint at E17.5 and fully developed at P1. At P1 tracer is seen along the proximal part of the MCAs, and from P8 CSF tracer reaches dorsal cortex via the MCA perivascular space. Cortical glymphatic influx occurs starting at P7 and increases during brain maturation.
(B) Aquaporin 4 (AQP4) polarization to astrocytes’ vascular endfeet increases with age. AQP4 polarization is more pronounced in the hippocampus than in the cortex at P1 and P7. Direction of CSF influx illustrated on the sagittal drawings; dashed green arrows show compartment flow entering hippocampus, possibly due to structural opening in P1 mice and further facilitated into the hippocampal parenchyma by AQP4 in the stratum radiatum and stratum moleculare. Solid green arrows visualize the glymphatic flow of CSF tracers facilitated by perivascular AQP4 water channels.
(C) Timeline represents some key developmental events in the mouse brain, with temporal orchestration shown in relation to the establishment of the glymphatic system (perivascular CSF tracer transport). Dashed lines indicate continued development at a reduced tempo, opposite to solid lines indicating an increase. CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; BBB, blood-brain barrier; HPC, hippocampus; CTX, cortex.