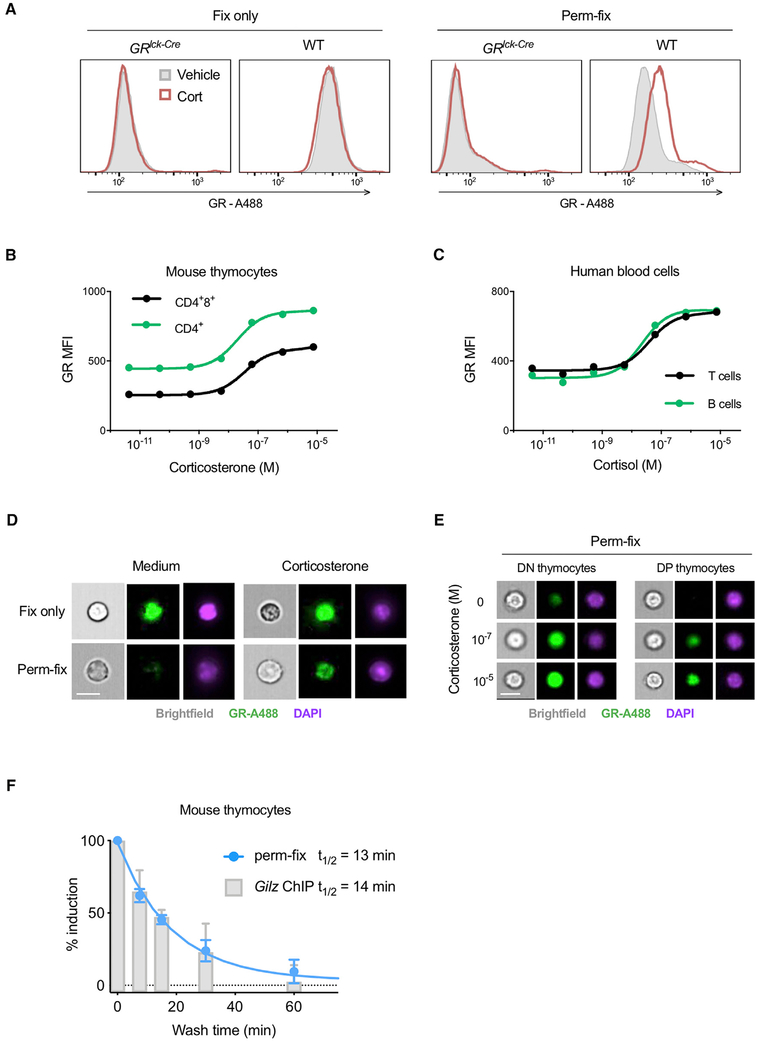
Figure 4. Permeabilization-Fixation of Primary Cells Allows Antibody Detection of Chromatin-Associated GR.
(A) Primary thymocytes from mice with T lymphocyte-specific deletion of the GR (GRlck-Cre) or wild-type (WT) mice were treated with corticosterone, fixed or perm-fixed, and stained for GR, and data were acquired by flow cytometry. Data are representative of two independent experiments.
(B and C) Primary mouse thymocytes (B) or primary human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (C) were treated with various glucocorticoid concentrations, surface stained, perm-fixed, and measured by flow cytometry. Estimated Kd values are 39 and 26 nM for mouse CD4+8+ and CD4+ thymocytes and 39 and 22 nM for human T and B cells, respectively. Data are representative of two independent experiments.
(D) WT mouse thymocytes were treated with corticosterone, surface stained, and fixed or perm-fixed, and data were acquired by imaging flow cytometry. Data are representative of two independent experiments. Scale bars, 10 μm.
(E) WT mouse thymocytes were treated with different corticosterone concentrations, surface stained, perm-fixed, and data were acquired by imaging flow cytometry. Data are representative of two independent experiments. Scale bars, 10 μm.
(F) WT mouse thymocytes were incubated for 20 min in medium containing 10−7 M corticosterone, then washed twice and incubated in steroid-free medium for the indicated times. One aliquot of cells was then fixed in 1% formaldehyde and ChIP-qPCR performed (as described in STAR Methods) to quantitate GR binding to the Tsc22d3 (Gilz) gene promoter, and another aliquot was perm-fixed, GR stained, and counted by flow cytometry. Data from both assays were normalized by setting the corticosterone-treated (unwashed) sample equal to 100% induction and the corticosterone-untreated sample set equal to 0% induction. Data are means ±SEM of three mice in two independent experiments.
See also Figure S2.