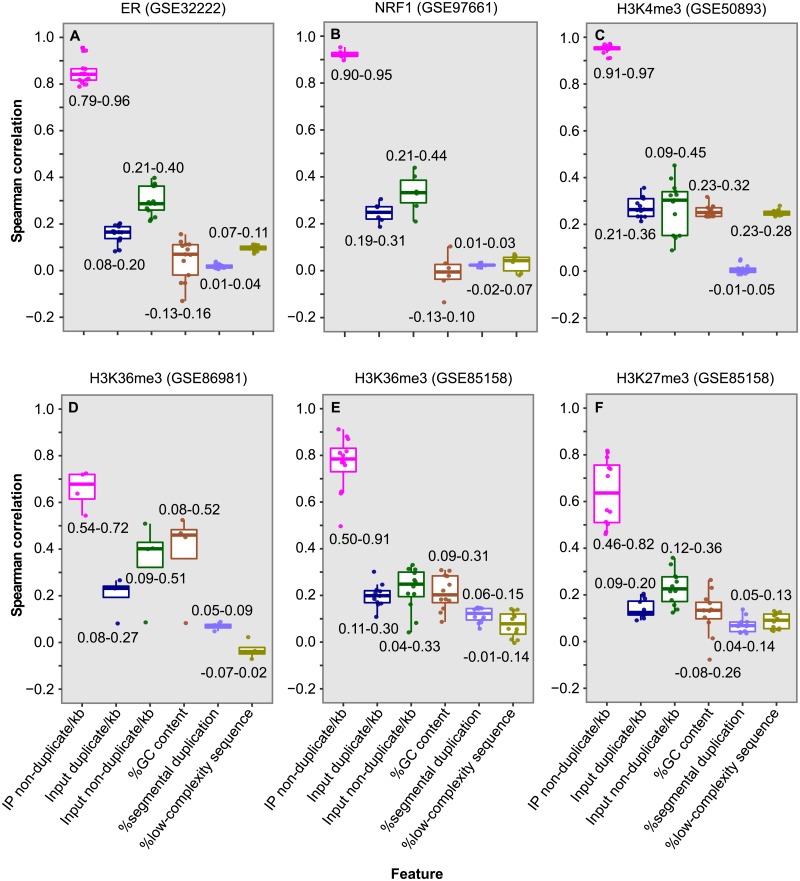
Fig 5. Box plot of Spearman rank correlation between duplicate level in peak and six factors.
(A) Thirteen ER libraries in breast cancer cell lines. (B) Six NRF1 libraries, including one in HepG2, two in MCF7 and three in K562. (C) Thirteen H3K4me3 libraries in lymphoblastoid cell lines. (D) Four H3K36me3 libraries in fetal retinal tissue. (E) Twelve H3K36me3 libraries in breast cancer cell lines. (F) Twelve H3K27me3 libraries in breast cancer cell lines. For each peak, duplicate level was estimated as the number of duplicates divided by peak size in kb, and non-duplicate level was estimated similarly. Duplicate and non-duplicate levels in peak corresponding regions in input were also calculated. GC content represents the number of guanine and cytosine bases divided by the total bases in a peak. Percentage of segmental duplication is the proportion of a peak that overlaps regions of segmental duplication, defined as those with > = 90% sequence identity over at least 1 kb (http://humanparalogy.gs.washington.edu/build37/build37.htm) [30]. Percentage of low-complexity sequence is the proportion of a peak that overlaps low complexity regions (https://figshare.com/articles/Low_complexity_regions_in_hs37d5/969685) [31].