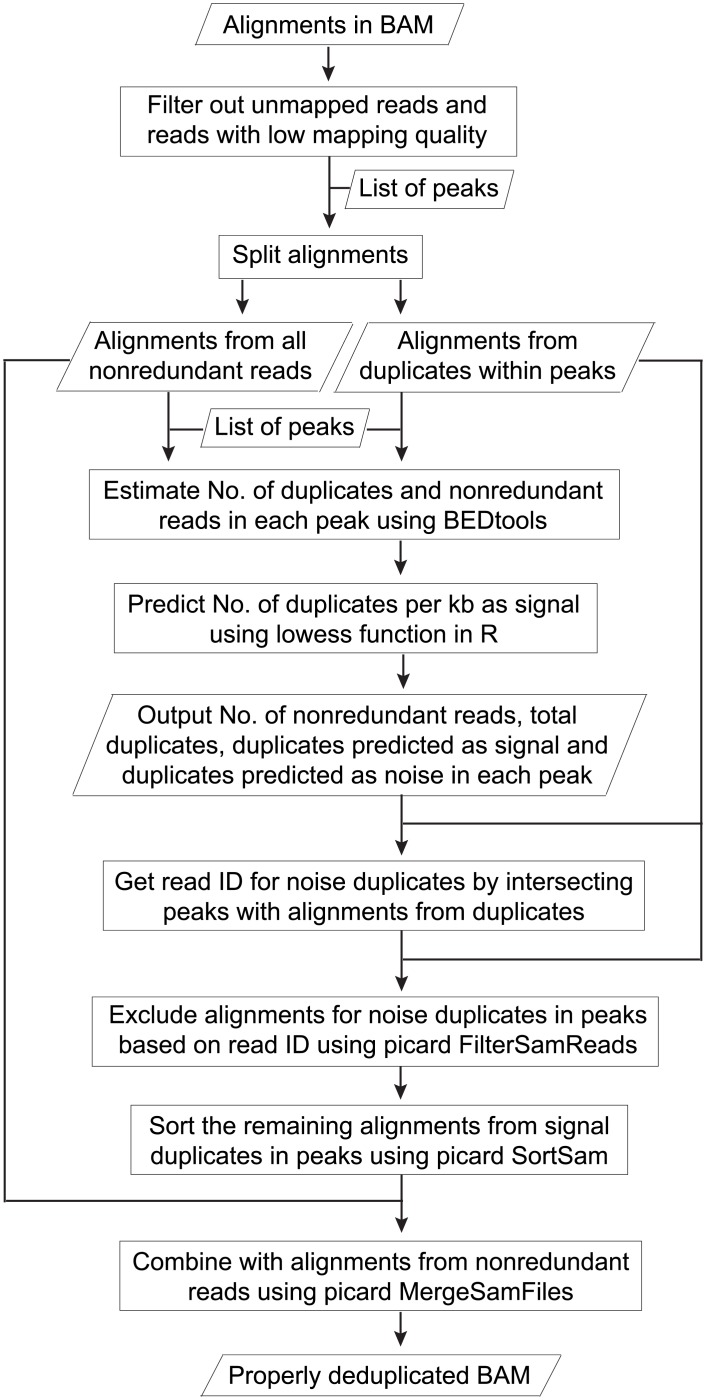
Fig 7. Flowchart for optimal deduplication in peaks.
The workflow takes a BAM file and a list of peaks as input. It outputs a table that shows the number of nonredundant reads (non-duplicates), duplicates predicted as signal and duplicates as noise for each peak. A properly deduplicated BAM file is also generated, which contains alignments for all nonredundant reads and for duplicates in peaks that are predicted as signal. For each peak, if N represents the predicted number of noise duplicates and S represents the predicted number of signal duplicates, a list of N read ID is randomly extracted from N+S duplicates mapped to that peak. Alignments for the noise duplicates are then excluded, and alignments for the remaining duplicates are combined with those from nonredundant reads.