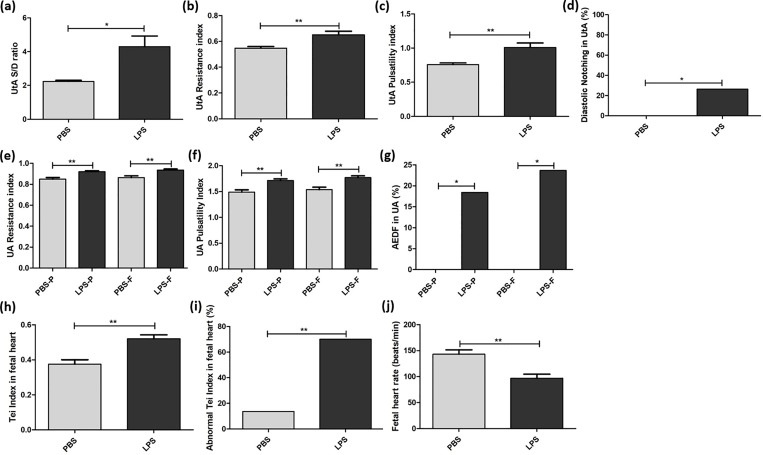
Fig 1. Uterine and umbilical artery insufficiency and abnormal Tei index of the fetal heart exposed to intrauterine inflammation.
Doppler waveforms were interrogated six hours after phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) or lipopolysaccharide (LPS) exposure. Doppler was used to assess the uterine artery (UtA), placental side of the umbilical artery (UA) and fetal side of the UA in the PBS group, as well as the UtA, placental side of the UA and fetal side of the UA in the LPS group. (a) The systolic/diastolic (S/D) ratio, (b) resistance indices, (c) pulsatility indices and (d) rate of early diastolic notch in UtA were determined for the LPS group (n = 17 dams, 34 arteries) and the PBS group (n = 8 dams, 16 arteries). (e) Resistance indices, (f) pulsatility indices and (g) the rate of absent end-diastolic flow (AEDF) were found for both the placental (-P) and fetal (-F) sides of the UA in the LPS group (n = 17 dams, 38 pups) and the PBS group (n = 8 dams, 26 pups). Time intervals of Tissue Doppler for evaluating Tei indices are shown for the PBS group and the LPS group. (h) Tei indices, (i) the rate of abnormal Tei index (>0.44) and (j) fetal heart rates were compared for the LPS group (n = 17 dams, 40 pups) and the PBS group (n = 8 dams, 22 pups). *p<0.05, **p<0.01.