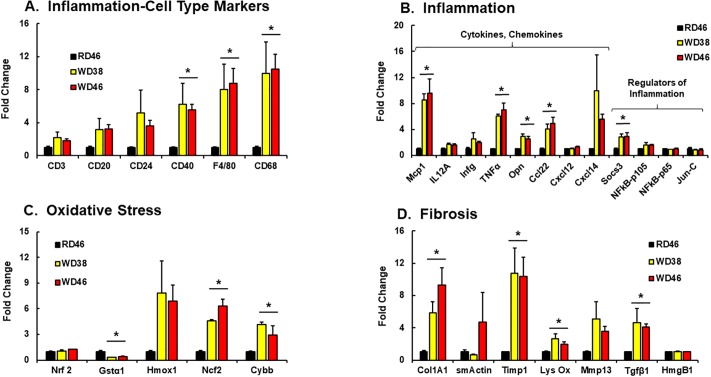
Fig 4.
Western diet effects on hepatic gene expression linked to inflammation (A & B), oxidative stress (C) and fibrosis (D). Hepatic transcripts were quantified by qRTPCR using cyclophilin as the reference gene. Transcript (mRNA) abundance is expressed as Fold Change (mean ± SEM, N = 7–8/group); *, FDR ≤ 0.05 versus the RD46 group. [A: CD3, T-cell marker; CD20, B-cell marker, CD24, granulocyte and B-cell marker, CD40, TNF-receptor superfamily marker; F4/80, macrophage/Kupffer cell marker; CD68, macrophage/Kupffer cell marker]. [B: Mcp1, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, Il12A, interleukin 12A, Infg, interferon γ; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor α; Opn, osteopontin; Cxcl12, ligand for chemokine C-X-C receptor 4; Cxcl14, ligand for a C-X-C chemokine receptor; Socs3, suppressor of cytokine signaling-3; NFκB-p105, mRNA encoding p50 subunit of NFκB; NFκB-p65, mRNA encoding p65 subunit of NFκB; Jun-C, Ap1 transcription factor]; [C: Nrf2, nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2; Gstα1, glutathione S transferase α1; Hmox1, heme-oxygenase 1; Ncf2, neutrophil cytosol factor 2 (p67 phox): Cybb, cytochrome B245, β-peptide (gp91-phos, Nox2)]; [D: Col1A1, collagen 1A1; smActin, smooth muscle actin; Timp1, tissue inhibitor metalloprotease-1; Lys Ox, lysyl oxidase; Mmp13, matrix metalloprotease-13; Tgfβ1, transforming growth factor β1; HmgB1, high mobility group protein B1].