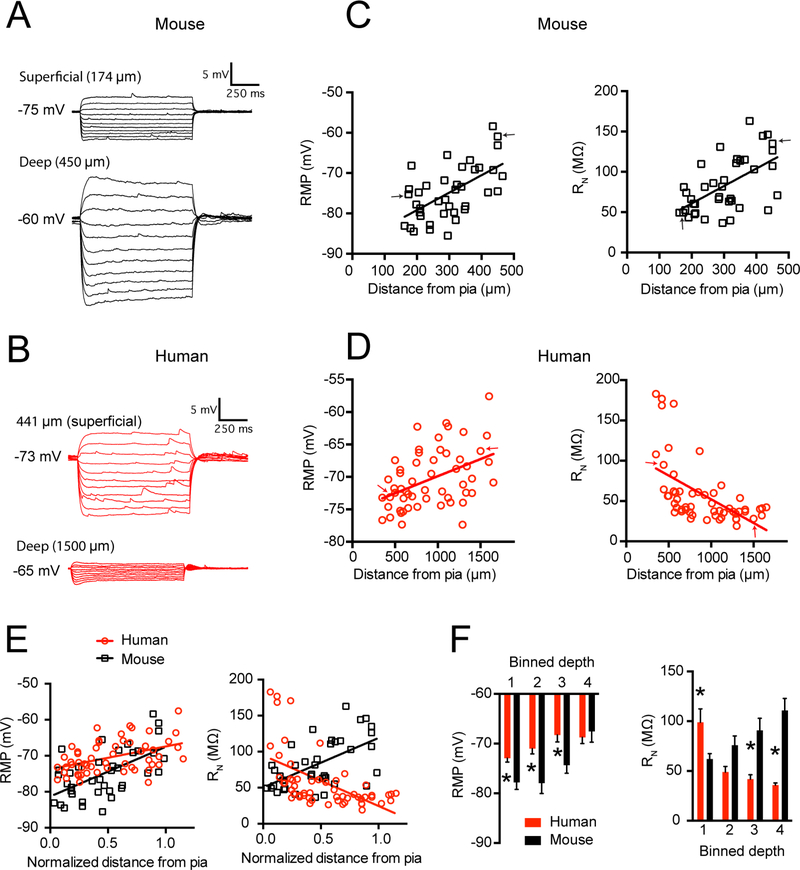
Figure 2 – Human and mouse supragranular pyramidal neurons display different subthreshold membrane properties.
Example voltage sweeps obtained from a superficial and deep supragranular pyramidal neuron in response to hyperpolarizing and depolarizing current injections in A) mouse TeA and B) human middle temporal gyrus. C) In mouse cortex, resting membrane potential and input resistance increase as a function of somatic distance from pia. D) In the supragranular layers of human middle temporal gyrus resting potential increases, but input resistance decreases as function of somatic distance from pia. Arrows correspond to sample voltage sweeps in A & B E) Resting potential and input resistance in mouse versus human cortex as a function of normalized somatic position in supragranular cortex. F) Data were binned into quarters based on the normalized distance of the soma from pia, where 1 is the most superficial quadrant and 4 is the deepest. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. * p < 0.0125, mouse versus human post-hoc t-test with Bonferroni correction.