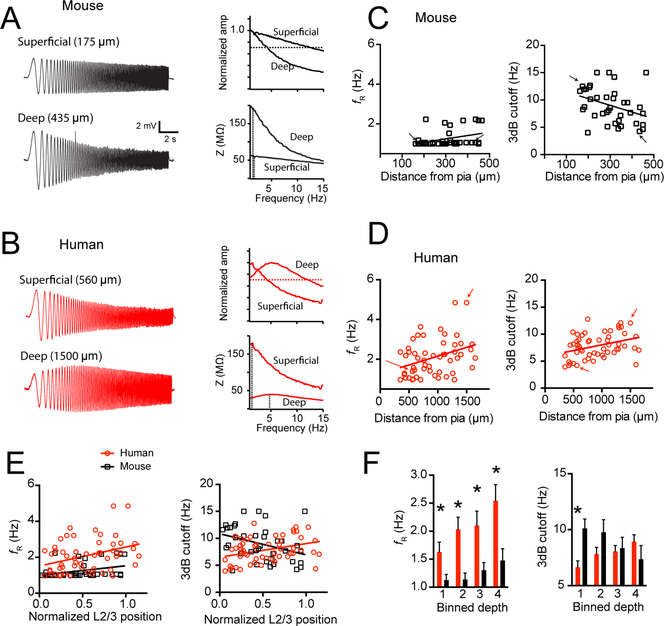
Figure 4 – Mouse and human supragranular pyramidal neurons display different subthreshold filtering properties.
Example voltage responses to a chirp stimulus current injection in a superficial and deep supragranular pyramidal neuron in A) mouse and B) human cortex. Impedance amplitude profile (ZAP) and normalized frequency response curves are also shown for these example neurons. Dotted lines mark the resonant frequency in the ZAP and the 3dB cutoff in the normalized frequency response curves. C) Mouse neurons were largely non-resonant and became more low-pass as a function of somatic depth from pia. D) Resonant frequency correlated with somatic depth from pia in human cortex. Additionally, in human cortex, 3dB cutoff frequency was correlated with somatic depth from pia. Arrows correspond to sample voltage sweeps in A & B. E) Resonant frequency and 3dB cutoff as a function of normalized depth from pia in mouse and human supragranular cortex. F) Data binned into quadrants and presented as mean ± SEM. For binned resonant frequency data * p < 0.001 mixed factor ANOVA effect of species. For binned 3 dB cutoff data * p < 0.0125, mouse versus human post-hoc t-test with Bonferroni correction.