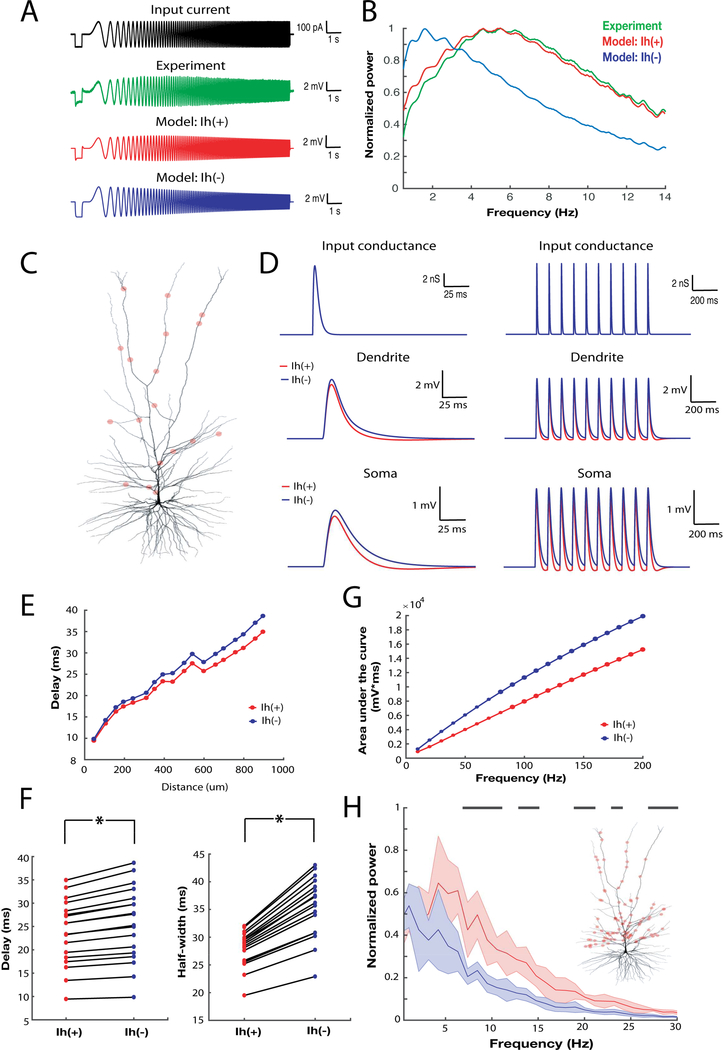
Figure 7 – Ih affects the subthreshold integrative properties of a morphologically precise human L3 pyramidal neuron model.
A) Voltage response elicited by somatic chirp stimulus of a L3 pyramidal neuron (green), biophysical model with Ih (red) and biophysical model without Ih. B) Power spectrum of somatic membrane potential response to chirp stimulus shown in A) (blue: experiment; green: Ih(+) model; red: Ih(−) model). C) Morphological reconstruction of a human L3 pyramidal neuron used for the simulations D) Single (left) or bursts (right) of AMPA-like conductances were injected at single synaptic locations (top) and the resultant local dendritic and propagated somatic voltage response were recorded in the Ih(+) (blue) and the Ih(−) model (red). The locations of 18 separate synaptic inputs are shown in panel C). E) The delay between the maximal amplitude of AMPA-like conductance and EPSPs peak recorded at the soma as a function of synaptic distance from soma in the Ih(+) (blue) and the Ih(−) model. F) Synaptic delays and half-width of the EPSPs calculated for Ih(+) and Ih(−) models. G) The integral of EPSPs recorded at the soma in response to bursts of synaptic input at various frequencies. The somatic response in the Ih(+) model was decreased relative to the Ih(−) model across several frequencies of synaptic input. H) Power spectrum of the somatic membrane potential of the Ih(+) and Ih(−) model when stimulated by 1000 synapses randomly located along the apical dendrite C). Black stripes correspond to statistically significant differences in the power spectrum (2 sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test; p<0.01). Inset: location of a subset (100 out of 1000) synapses is shown. Data are presented as mean ± SD.