Figure 1: Schematic overview of the BMP signaling system and associated transcription factors relevant for adipogenesis.
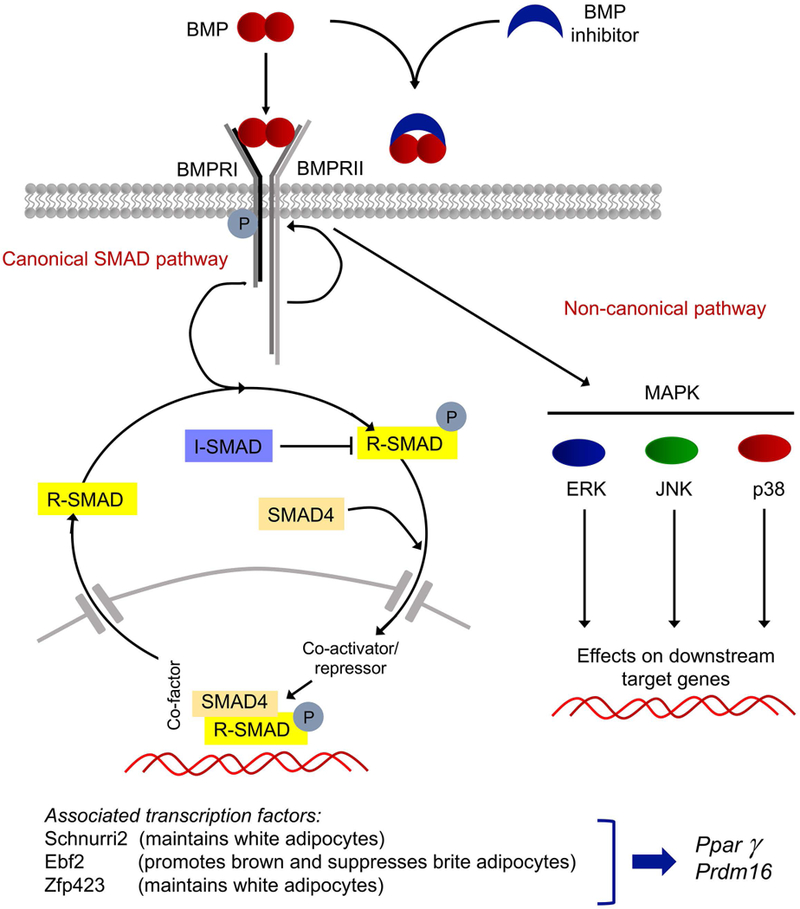
Top, BMP dimers bind to a complex consisting of BMPRI and BMPRII, or are sequestered by BMP inhibitors. In canonical BMP signaling, the type II receptor phosphorylates (activates) the type I receptor, which in turn activates regulatory SMAD1/5/8. The R-SMADs combine with SMAD4, a co-SMAD, and enters the nucleus to regulate gene expression together with the appropriate co-activators and repressors. The R-SMADs can also be inhibited by the I-SMADs. In non-canonical BMP signaling, MAPK, ERK, JNK, and p38 are activated. Bottom, transcription factors known to affect adipocyte differentiation. BMP, bone morphogenetic protein; BMPRI, BMP type I receptor; BMPRII, BMP type II receptor; R-SMAD, regulatory SMAD; I-SMAD, inhibitory SMAD; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; JNK, Jun N-terminal kinase; p38, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; Ebf2, early B-cell factor 2; Zfp423, zinc finger protein 423; Pparγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ; Prdm16, PR domain containing 16.
