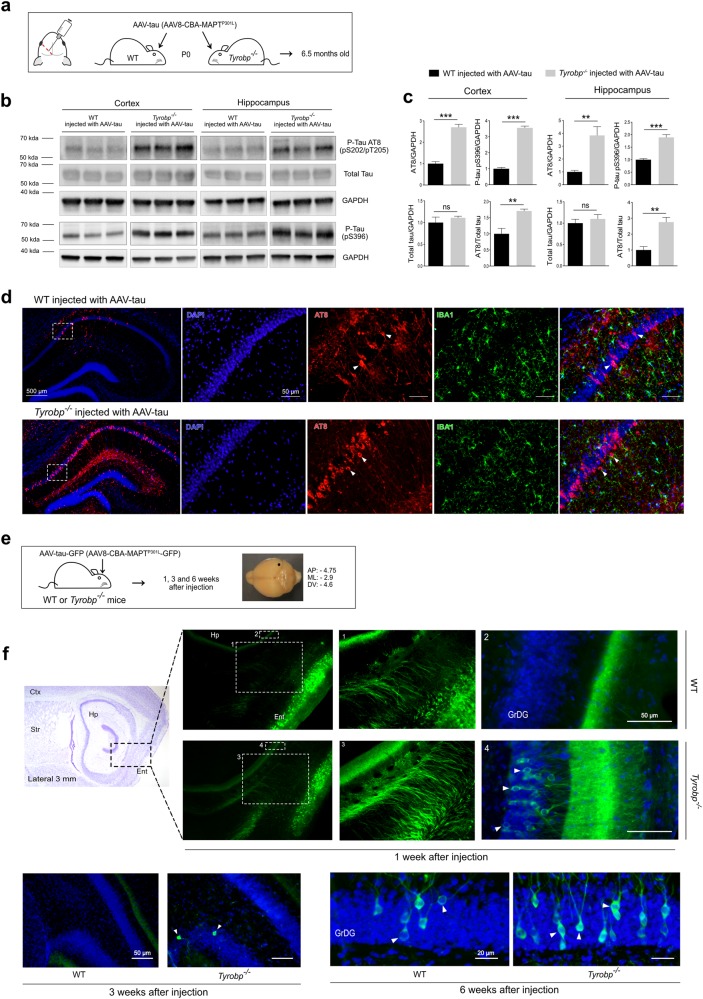
Fig. 2.
TYROBP deficiency promotes tau phosphorylation and spread in AAV-tau-based mouse models of tauopathy. a Wild-type or Tyrobp-/- P0 pups received intracerebroventricular injections of AAV8-TauP301L (designated AAV-tau) using a chicken β-actin (CBA) promoter. Brains were examined at age 6.5 months. b Representative western blots of extracts from cortical and hippocampal regions of wild-type (WT) or Tyrobp-/- mice injected with AAV-tau using antibodies as indicated: antibody AT8 (detects paired helical filament epitopes of tau phosphorylated at residues serine 202 and/or threonine 205); antibody anti-tau (phospho S396) (detects tau phosphorylated at residue serine 396); antibody T46 (detects total tau); anti-GAPDH. Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Figure 2. c Densitometric analyses of P-tau western blots standardized to GAPDH or total tau. n = 5 (WT and Tyrobp-/-) for extracts from hippocampus and n = 4 (WT) or n = 5 (Tyrobp-/-) for extracts from cortex. Error bars represent means ± SEM. Both males and females were used, and analysis was performed on combined results. Statistical analyses were performed using a Student’s t-test, **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ns nonsignificant. d High magnification of coronal sections of hippocampi showing increased AT8 staining in Tyrobp-/- mice injected with AAV-tau. Scale bar: hippocampus = 500 μm and high magnification = 5 μm. e AAV8-TauP301L-GFP (designated AAV-tau-GFP) was injected in the medial entorhinal cortex to study the spread of tau from this structure to the hippocampus. AP anteroposterior, ML mediolateral, DV dorsoventral. The perforant pathway connecting these two regions is implicated in this spread, although the diffuseness of the immunoreactivity raises the possibility that spread may occur via the interstitium in addition to (or instead of) via neuronal uptake and transneuronal propagation along the classical neuroanatomic pathway. f Wild-type or Tyrobp-/- mice were injected with AAV-tau-GFP at 4 months of age, and brains were examined at 1, 3 or 6 weeks after injection (n = 3 per group). Males and females were used for experiments, and results were combined for analysis. Ctx cortex, Str striatum, Hp hippocampus, Ent entorhinal cortex, GrDG granule cell layer of the dentate gyrus