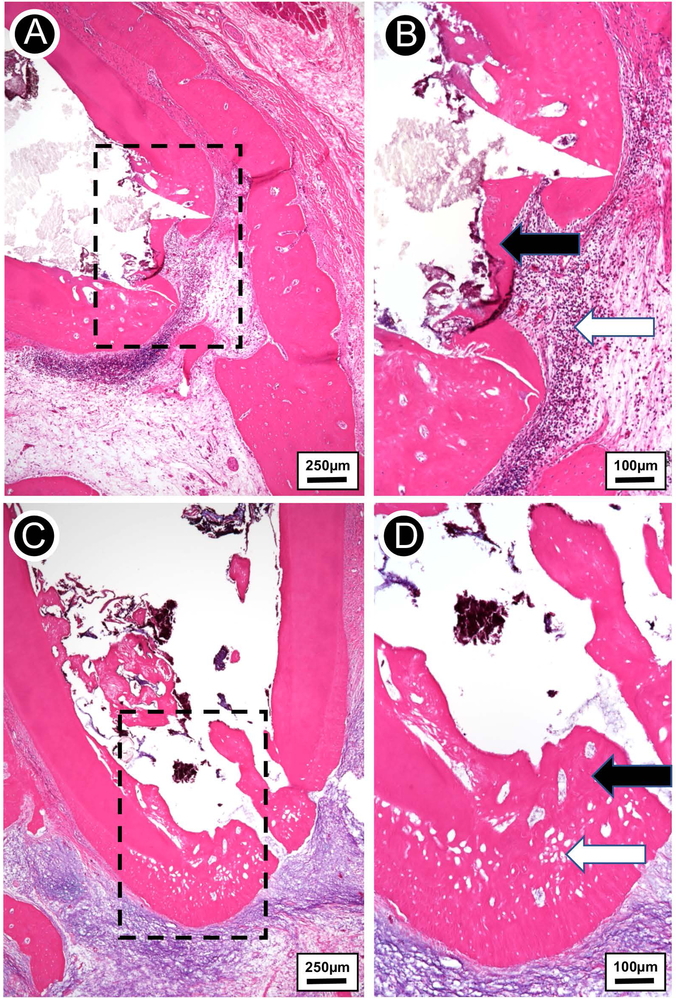
FIGURE 8.
(A) Hematoxylin-eosin stained micrograph of extracted infected tooth treated with TAP solution, showing a thin bridge of apical osteodentin with early periapical bone destruction. (B) Higher magnification view of the rectangular area from A. Thin irregular osteodentin bridge at root apex (black arrow) and adjacent chronically inflamed granulation tissue and collections of neutrophils (white arrow). (C) Hematoxylin-eosin stained micrograph of extracted infected tooth treated with the tubular 3D triple antibiotic-eluting construct, showing thick layer of regenerated osteodentin restoring the outline of the root apex. The osteodentin demonstrates cellular inclusions and resembles a combination of bone, osteoid, predentin, and dentin. (D) Higher magnification view of the rectangular area from C. Complete regeneration of apical root structure (thick osteodentin layer; black arrow). The regenerated osteodentin recapitulates the normal root apex outline with well-developed osteodentin containing cellular inclusions (white arrow).