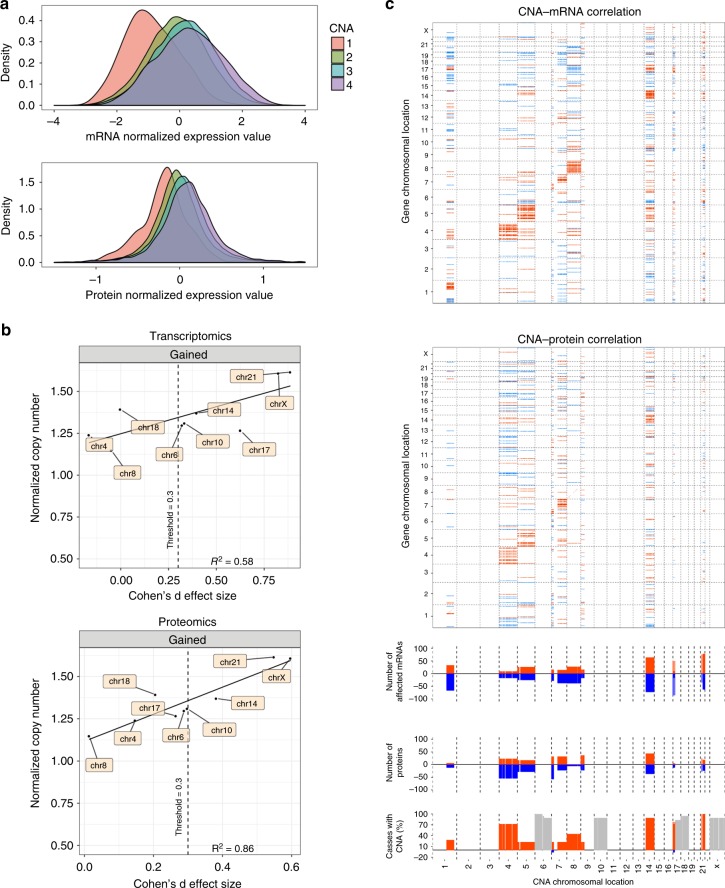
Fig. 2.
Effects of copy number alterations on mRNA and protein abundance. a Dosage effects in 18 high hyperdiploid ALL at the RNA and protein levels. The effects were lower on the protein level than on RNA level, showing additional layers of control for protein expression. b Cohen’s d effect size analysis of gained chromosomes in high hyperdiploid vs. ETV6/RUNX1-positive leukemia. c cis and trans effects of copy number changes in 18 cases of hyperdiploid childhood B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Correlations of copy number aberrations (CNA) (x-axes) to RNA (top) and protein (bottom) expression levels (y-axes) are shown. Note that a large fraction of the genome was not included in the analysis since there was no copy number variance, either because all cases had two copies or because all cases had three copies. Significant (multiple-test adjusted P < 0.05) positive (red) and negative (blue) correlations between CNA and mRNAs/proteins are indicated. CNA cis effects appear as a red diagonal line, CNA trans effects as vertical stripes. The fraction (%) of significant CNA trans effects (positive in red and negative in blue) for each CNA gene is shown below. The bottom panel shows the fraction (%) of leukemias harboring CNA (copy number gain in red and copy number loss in blue). Chromosomes that were gained in more than 16 cases were not informative; their copy number is shown in gray