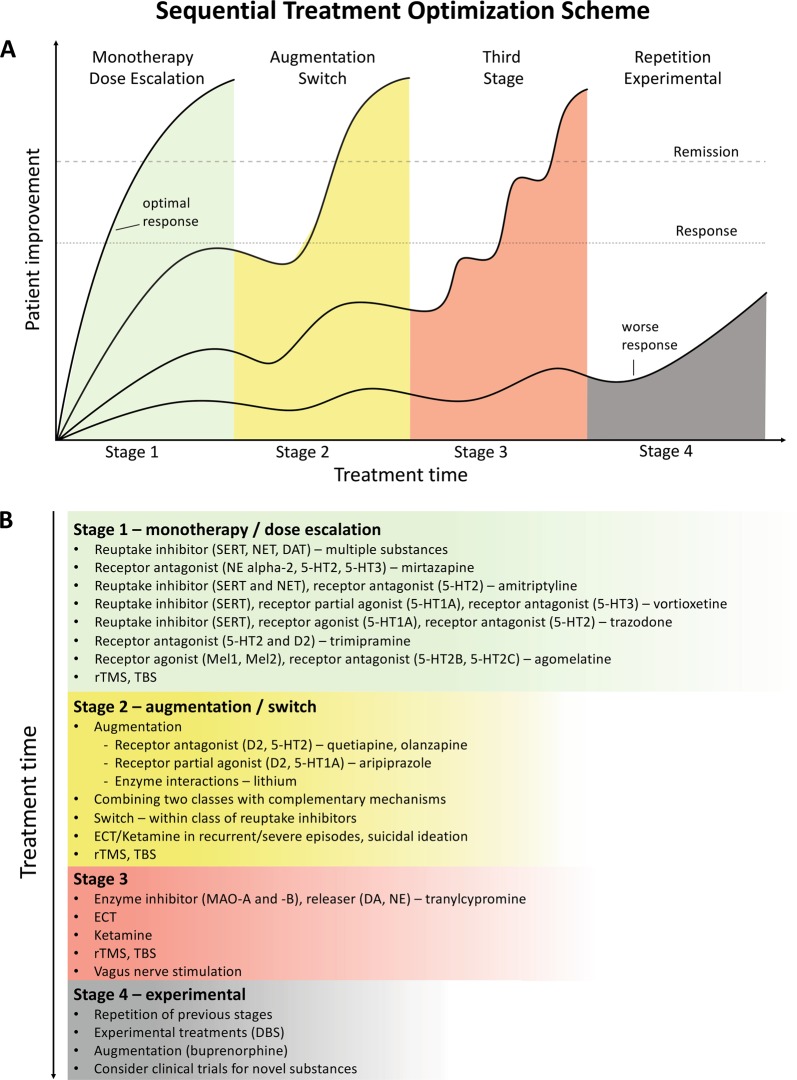
Fig. 3. Sequential treatment optimization scheme for major depression.
A sequential treatment optimization scheme was generated based on antidepressant treatment guidelines (see Table 2). Treatment optimization is possible for patients being treated for the first time but also for patients with insufficient response to first- or second-stage therapies. a Treatment response curves for four common types of patients highlight the importance of sequentially introducing the next step upon non-response to previous steps. b Currently available treatments are listed in neuroscience-based nomenclature201 with treatment lines corresponding to improvement curves in a. Although current classifications vary, patients classified as having treatment-resistant depression (TRD) are eligible for second- or third-stage therapies. 5-HT1A and similar: serotonin receptor subtypes; DBS: deep brain stimulation; DAT: dopamine transporter; D2: dopamine receptor D2; ECT: electroconvulsive therapy; MAO: monoamine oxidase; NET: noradrenaline transporter; SERT: serotonin transporter; TBS: theta-burst stimulation; rTMS: repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation; DA: dopamine; NE: norepinephrine.