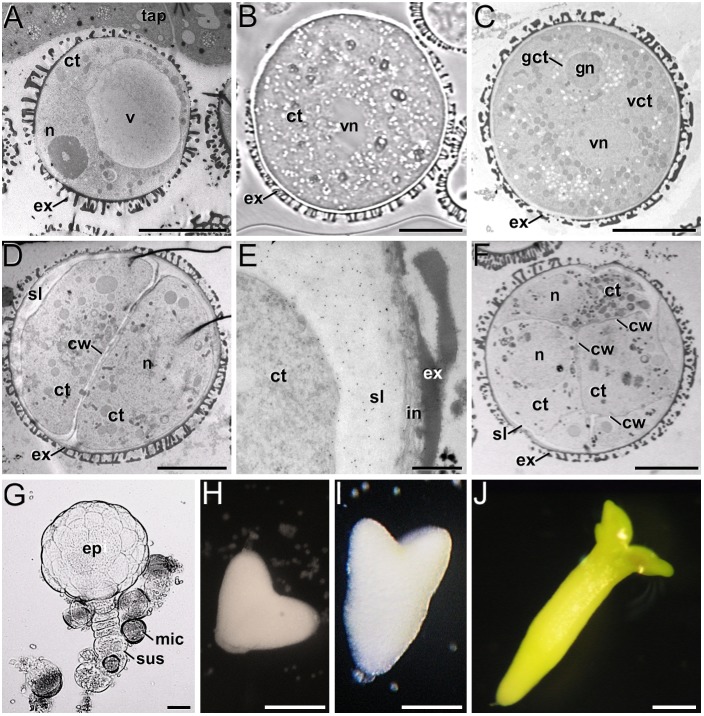
FIGURE 1.
B. napus in vivo microspores and pollen, and development of microspore cultures. (A) In vivo vacuolated microspore, still within the anther locule and surrounded by tapetum (tap). (B) In vitro pollen-like structure. The only nucleus visible in this section is the vegetative nucleus (vn). (C) In vivo pollen grain. Note the generative nucleus (gn) within the cytoplasm of the generative cell (gct), and the vegetative nucleus (vn), all embedded within the cytoplasm of the vegetative cell (vct). (D) 2-celled embryogenic microspore, with a newly formed inner cell wall (cw) and a thick subintinal layer (sl). (E) Anti-callose immunogold labeling in a 2-celled embryogenic microspore, revealing the abundance of callose in the subintinal layer. (F) Multicellular structure of around 8-10 cells. (G) Suspensor-bearing globular MDE surrounded by dead or arrested microspores (mic), and showing the embryo proper (ep) and suspensor (sus) domains. (H) Heart-shaped MDE. (I) Torpedo MDE. (J) Cotyledonary MDE. ct: cytoplasm; ex: exine; n: nucleus; v: vacuole. Bars: (A–D): 10 μm; (E): 500 nm; (F): 10 μm; (G): 20 μm; (H–J): 200 μm.