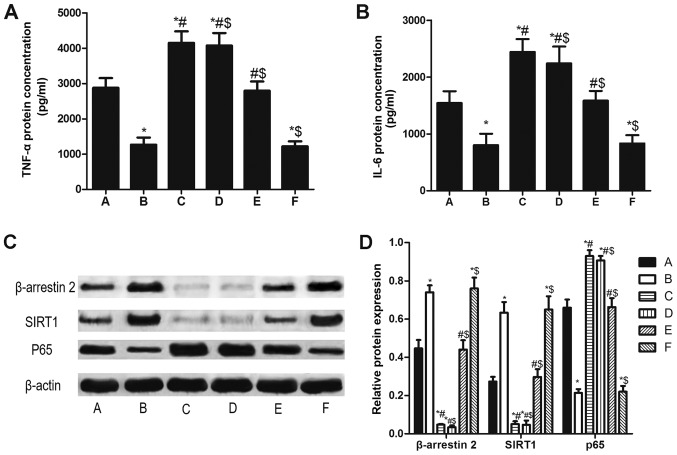
Figure 5.
β-arrestin 2 siRNA increases TNF-α, IL-6 and p65, and decreases SIRT1 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. The concentration of (A) TNF-α and (B) IL-6. (C) Qualitative and (D) quantitative analysis of western blotting results for β-arrestin 2, SIRT1 and P65. The groups were as follows: A, LPS stimulation for 48 h; B, LPS stimulation for 48 h and Tan IIA treatment for another 24 h; C, β-arrestin 2 siRNA incubation for 4 h and LPS stimulation for 48 h; D, β-arrestin 2 siRNA incubation for 4 h, LPS stimulation for 48 h and Tan IIA treatment for another 24 h; E, negative control siRNA incubation and LPS stimulation for 48 h; E, negative control siRNA incubation, LPS stimulation for 48 h and Tan IIA treatment for another 24 h. *P<0.05 vs. A group; #P<0.05 vs. B group; $P<0.05 vs. C group. si, small interfering; SIRT1, NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1; p65, transcription factor p65; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; IL, interleukin; Tan IIA, tanshinone II A; LPS, lipopolysaccharides.