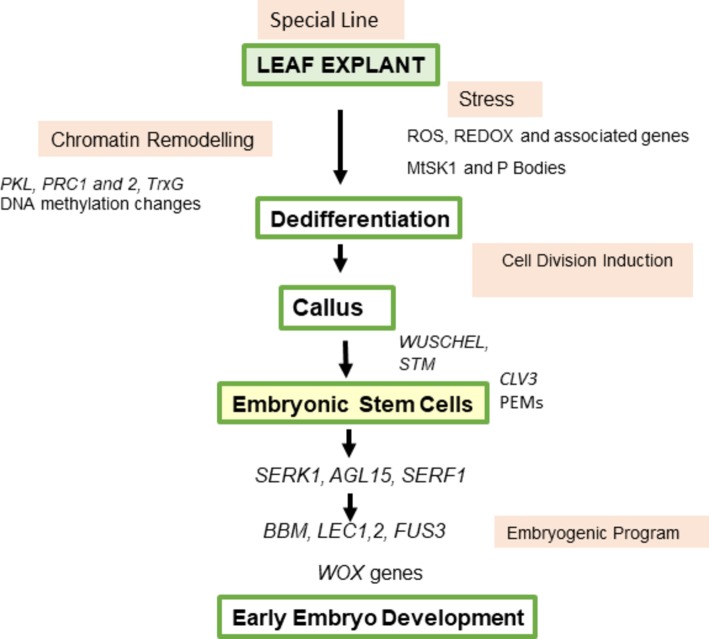
Figure 5.
Model for sequence of events in somatic embryogenesis from M. trunctula leaf explants. Excision and plating of the explant produce ROS that probably in interaction with hormones cause chromatin remodeling involving PKL, PRC complexes, and TRITHORAX genes, and a stress kinase that maybe linked to transcript degradation via RNA processing bodies. Cell divisions follow and callus is produced. Cytokinin-dependent WUS expression is essential for SE and there is an initial expression analogous to that occurring in the ovule followed by stem cell development linked to PEMs in patches on the callus, correlating with CLV3 and STM expression. AGL15, SERK, and SERF are part of the correct hormone milieu leading to expression of BBM and LEC genes and the embryogenic program. The changes diagramed go hand in hand with hormonal changes. Auxin is initially high then lowers as differentiation starts, followed by auxin regulation associated with embryo patterning in the formation of the bipolar embryo. Cytokinin is important for specific genes and the cell cycle. Endogenous ethylene is produced and endogenous ABA/GA ratios specific to M. truncatula influence SE. Ethylene, ABA, and GA can be involved in regulating auxin responses. Abbreviations are in the text.