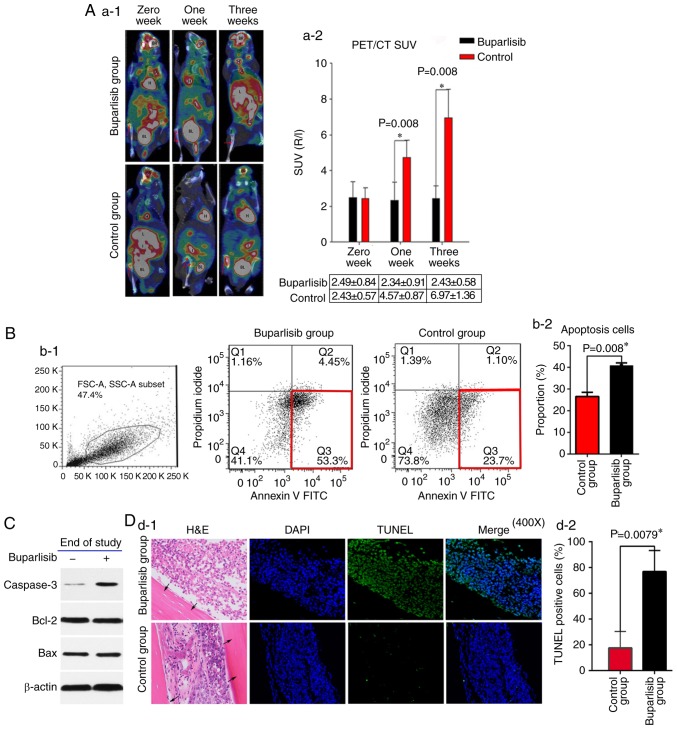
Figure 2.
Buparlisib induces NCI-H460 cell apoptosis and reduces tumour activity in vivo. (A-1) 18F-FDG PET/CT of bone tumour-bearing mice was assessed at different time points in buparlisib-treated and control mice; red arrows represent the boundaries of the ROI. Tumour burden was reduced in the ROI of the buparlisib group compared with the control group at 1 and 3 weeks. High 18F-FDG uptake is considered normal in organs including the H, BR, BL and I. (A-2) Quantitative R/L ratio of SUV of bone tumour-bearing mice was assessed at the indicated time points. (B-1) Apoptotic cell death was assessed in single cell suspensions from excised tumour lesions of bone tumour-bearing mice at the end of study. NCI-H460-luc2 tumour cells were randomly isolated from three mice obtained from each group at 3 weeks after treatment, and were stained with Annexin V and analysed by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. The red frame in the right lower corner in each group indicated early apoptosis. (B-2) Quantification of data from the apoptosis assay. (C) Western blotting of tumour lesions obtained from both groups of bone tumour-bearing mice at the end of study. Caspase 3 expression, but not Bcl-2 and Bax expression, was increased in the buparlisib group at 3 weeks. β-actin was used as a loading control to ensure equal loading between samples. (D-1) Tibia sections of intraosseous NCI-H460 tumours obtained from buparlisib and control group mice at 3 weeks were stained with TUNEL and DAPI. Blue fluorescence indicated nuclei stained with DAPI. Green fluorescence indicated TUNEL-positive NCI-H460 cells in the bone marrow cavity. Black arrows indicated the cortical wall of tibiae. Magnification, ×400. (D-2) Quantification of TUNEL-positive NCI-H460 cells from both groups of bone tumour-bearing mice at the end of study. The percentage of TUNEL-positive cells was higher in the buparlisib group compared with in the control group at 3 weeks. Data are presented as the means ± standard deviation. *P<0.05. 18F-FDG, 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose; A, artery; Bax, Bcl-2-associated X protein; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; BR, brain; BL, bladder; FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; H, heart; H&E, haematoxylin and eosin; I, intestines; J, joint; L, liver; PET/CT, positron emission tomography/computed tomography; R/L, right/left; ROI, region of interest; SUV, standardized uptake value; TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate nick end labelling.