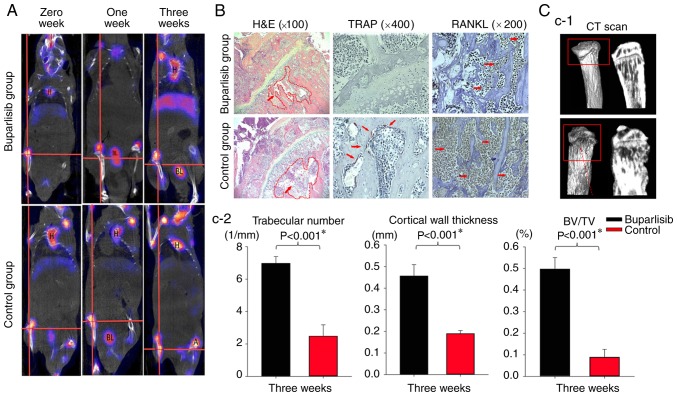
Figure 3.
99mTc-MDP SPECT/CT imaging of bone tumour-bearing mice during the whole study, and H&E staining, IHC and ex vivo MicroCT of tumour lesions at the end of the study. All regions shown on the histological slices were in the metaphysis. (A) 99mTc-MDP SPECT/CT imaging of both groups of bone tumour-bearing mice at different time points. SPECT/CT imaging of the mice highlighted increased radioactive uptake in the control group compared with the buparlisib group, particularly at 3 weeks, as indicated at boundaries of a region of interest, which was marked with a red cross in the centre. Organs including the H, brain, BL, liver and intestines exhibited a high uptake of 99mTc-MDP, which is considered normal. (B) H&E and IHC staining of tumour lesions at the end of the study. H&E staining revealed that more tumour cells were detected in the control group and the adjacent bone marrow cavity exhibited a loss of trabecular bone (×100 magnification; red arrows indicate tumour cells and the red dotted circle indicates the location of the marrow cavity). The protein expression levels of TRAP and RANKL were examined by IHC (red arrows indicate positive staining). The osteoclast marker TRAP was expressed in the activated osteoclast cells at the tumour bone interface, as indicated by dark purple staining. The other osteoclast marker, RANKL, exhibited dark brown staining. The levels of osteoclast markers were decreased in the buparlisib group. (C-1) Ex vivo MicroCT of tumour lesions at the end of study. MicroCT analysis of the proximal tibia of tumour-bearing mice revealed a marked reduction in the number of osteolytic bone lesions in the buparlisib group. Red dotted arrow in the red border indicates osteolytic bone lesions in the control group. (C-2) Quantitative analysis of ex vivo MicroCT of tumour lesions at the end of the study. Trabecular number, cortical wall thickness and BV/TV were measured in the proximal tibia of tumour-bearing mice. The number of osteolytic bone lesions was decreased in buparlisib-treated mice compared with in control mice. Data are presented as the means ± standard deviation. *P<0.05. 99mTc-MDP, 99mTc-methylene diphosphonate; A, artery; BL, bladder; BV/TV, bone volume/total volume; CT, computed tomography; H, heart; H&E, haematoxylin and eosin; IHC, immunohistochemistry; RANKL, receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand; SPECT, single-photon emission computed tomography; TRAP, tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase.