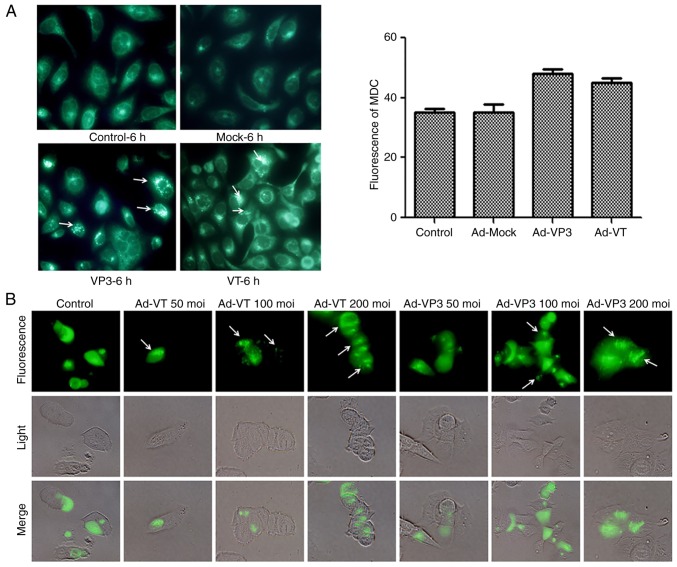
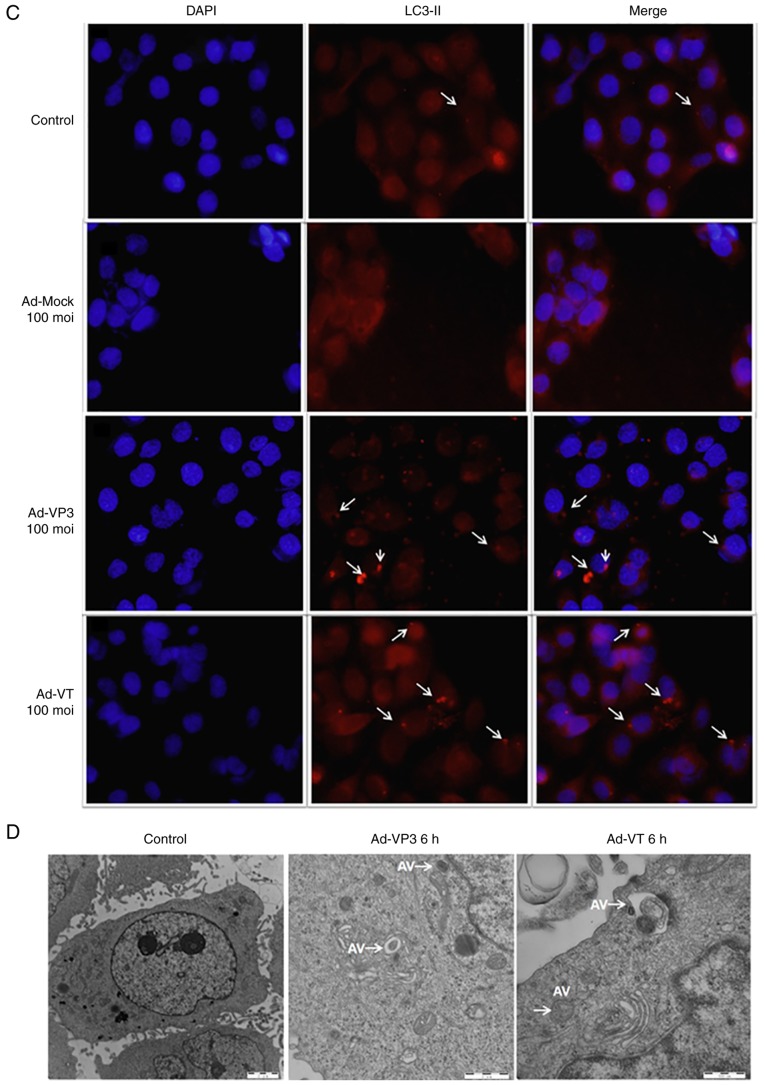
Figure 4.
Apoptin induces autophagy in MCF-7 cells. (A) To evaluate autophagic vacuoles, MCF7 cells were infected with Ad-MOCK, Ad-VT, and Ad-VP3 (100 MOI) for 6 h and stained with MDC. The graph shows the percentage of MDC-stained autophagic corpuscles in MCF-7 cells in the various groups after 6 h (magnification, ×40). (B) MCF-7 cells were transfected with pEGFP-LC3B for 24 h and then infected with carious concentrations Ad-VT or Ad-VP3 (50, 100, and 200 MOI) for 6 h. pEGFP-LC3 signals were observed by fluorescence microscopy (magnification, ×40). Apoptin induces autophagy in MCF-7 cells. (C) Representative images of immunocytochemistry. Visualization of LC3 by fluorescence microscopy. MCF-7 cells were infected with Ad-MOCK, Ad-VT and Ad-VP3 (100 MOI) for 6 h and stained with an antibody recognizing LC3 for 18 h post-treatment. The control cells exhibited diffuse cytosolic LC3 distribution. Ad-VP3-infected cells exhibited an increase in the number of cells with LC3 dots, whereas the number of cells with LC3 dots was further increased upon Ad-VT exposure. Red fluorescence indicates the presence of the LC3 protein (magnification, ×40). (D) Transmission electron microscopy revealed autophagosome ultrastructures in the enlarged images following infection of cells with Ad-VT or Ad-VP3 for 6 h. Control: magnification, ×5,000; Ad-VT and Ad-VP3: magnification, ×10,000. Ad-VP3, Ad-Apoptin; Ad-VT, Ad-Apoptin-hTERTp-E1a; LC3, microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3; MDC, monodansylcadaverine; MOI, multiplicity of infection; pEGFP-LC3, enhanced green fluorescence protein-LC3 plasmid.