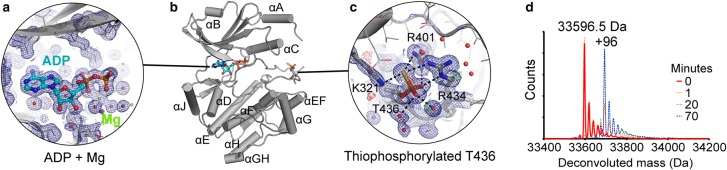
Figure 4. Crystal structure of the PAK3 KD (grey) and key features.
(a) PAK3 KD was crystallised in the presence of magnesium and ATP-γ-S, which was converted to ADP (cyan). Blue mesh = 2Fo − Fc electron density map contoured at 1σ within 4 Å of ADP molecule, green and red mesh = Fo − Fc positive and negative difference map contoured at 3σ. Red spheres = water molecules, green spheres = magnesium ions. (b) Overview of the crystal structure showing the placement of ADP and the thiophosphorylated activation loop. (c) Details of thiophosphorylated residue, T436, including electron density 2Fo − Fc map (blue mesh), positive (green mesh) and negative (red mesh) difference density Fo − Fc map and key hydrogen-bonding interactions (black dotted lines). (d) Overlaid denaturing mass spectra of PAK3 KD incubated in solution with ATP-γ-S and magnesium, taken at various time points. PAK3 rapidly auto-thiophosphorylates using ATP-γ-S, leading to covalent addition of a thiophosphate group (+96 kDa).