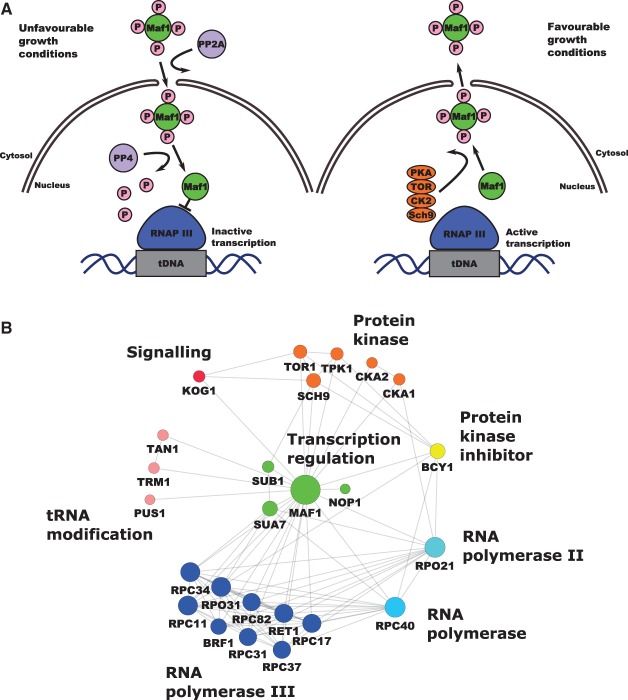
Figure 1. RNAP III regulation by Maf1 and Maf1 interaction network.
(A) RNAP III transcription repression is regulated by Maf1. Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation events are involved in the mobility and transportation of Maf1 through the nuclear membrane in which a group of protein kinases are involved in the control of Maf1 nuclear localization responding to stress events. Maf1 produces transcriptional repression on RNAP III by inducing conformational changes. (B) Maf1 protein–protein interaction network. Experimental interactions from STRING database are shown. Nodes have been colored by protein activity in which different protein complexes related to tRNA modification and transportation can be observed. green: transcription regulation; MAF1: negative regulator of RNAP III, SUB1: Sub1 transcriptional regulator facilitating elongation through factors that modify RNAP II, role in hyper-osmotic stress response through RANP II and RNAP III, negatively regulates sporulation [19–21], NOP1: Nop1, histone glutamine methyltransferase, modifies H2A at Q105 in nucleolus that regulates transcription from the RNAP I promoter involved in C/D snoRNA 3′-end processing. Essential gene leads to reduced levels of pre-rRNA species and defects in small ribosomal subunits biogenesis [22–24], SUA7: transcriptional factor TFIIB, a general transcription factor required for transcription initiation and start site selection by RNAP II [25,26] — Sub1 interaction with TFIIB [27]. Marine blue: RNAP III holoenzyme subunits, red: protein kinases, KOG1: Kog1 the component of the TPR complex, Kog1 depletion display the starvation-like phenotypes — cell growth arrest, reduction in protein synthesis, glycogen accumulation, up-regulation in the transcription of nitrogen catabolite repressed and retrograde responses genes conserved in from yeast to man is the homolog of the mammalian TORC1 regulatory protein RAPTOR/mKOG1 [28,29], TOR1 mediates cell growth in response to nutrient availability and cellular stress by regulating protein synthesis, ribosome biogenesis, autophagy, transcription activation cell cycle [30,31] . Yellow: PKA kinase inhibitor protein BCY1, pink: tRNA modification TAN1: tRNA modifying proteins Tan1 (responsible for tRNASER turnover [32]), TRM1: Trm1 tRNA methyltranspherase produces modified base N2, n2 dimethylguanosine in tRNA in nucleus and mitochondrion [33], PUS1: PUS1 associated with human disease [34], introduces pseudouridines in tRNA, also as on U2 snRNA and pseudouridylation of some mRNA [35,36]. Blue: RPC40 (AC40) is a common subunit to RNAP I and III conserve in all eukaryotes [37,38]. Light blue: RPO21: largest subunit of RNAP II, which produces all nuclear mRNAs, most snoRNAs and snRNA and the telomerase RNA encoded by TLC1 [39,40] (according to Saccharomyces Genome Database).