Fig. 10.
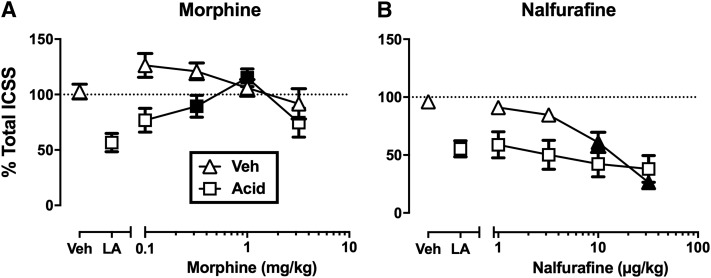
The assay of pain-depressed ICSS can dissociate analgesics from nonanalgesics. (A and B) Effects of the μ opioid receptor agonist analgesic morphine (A) and the κ opioid receptor agonist nonanalgesic nalfurafine (B) in rats treated with intraperitoneal lactic acid (LA) or with lactic acid vehicle (Veh). Abscissae show the dose in milligrams per kilogram. Ordinates show the percentage of total ICSS reinforcements collapsed across all brain-stimulation frequencies as shown in Fig. 9D. Treatment with lactic acid alone depressed ICSS, whereas vehicle treatment did not. Morphine blocked acid-induced ICSS depression in acid-treated rats at doses that did not affect ICSS in vehicle-treated rats. Conversely, nalfurafine failed to block acid-induced depression of ICSS up to doses that significantly decreased ICSS in vehicle-treated rats. Filled symbols indicate significant differences from LA in (A) or from Veh in (B) (P < 0.05). Data adapted from Altarifi et al. (2015) and Lazenka et al. (2018).