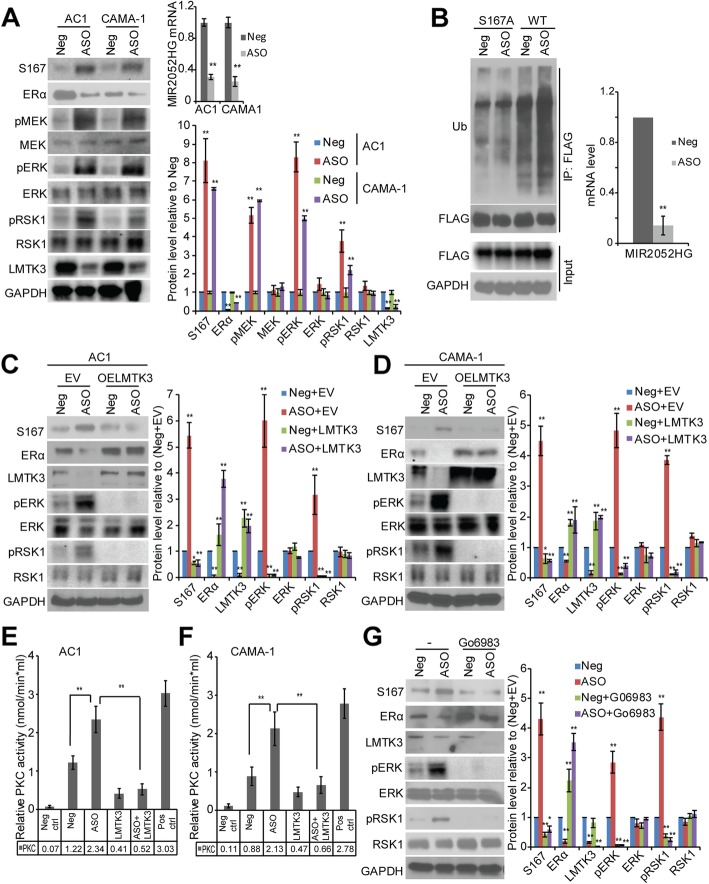
Fig. 4.
MIR2052HG regulates ERα protein stability through MEK/ERK/RSK1 pathway. a Knockdown of MIR2052HG increased phosphorylation of MEK, ERK, RSK1, as well as ERα S167 and decreased LMTK3 total level in MCF7/AC1 and CAMA-1 cells. Protein levels were quantified as described in Fig. 3. Error bars represent SEM. The significant difference between Neg and ASO is indicated by **p < 0.01. b Knockdown of MIR2052HG promoted the ubiquitination of wild-type ERα, but not ERα S167A mutant. 293 T cells were transfected with HA-Ub plasmid and FLAG-ERα or FLAG-ERα S167A plasmid and then transfected with either the MIR2052HG specific ASOs or the negative control ASO followed by MG132. Wild-type or S167A mutant ERα proteins were immunoprecipitated and analyzed by western blot. Knockdown efficiency in 293 T cells was determined by qRT-PCR. c–d Overexpression of LMTK3 in MIR2052HG knocked-down MCF7/AC1 (c) and CAMA-1 (d) cells reversed ERα protein levels and the phosphorylation of MEK, ERK, RSK1, and ERα S167. Overexpression of LMTK3 was determined by western blot analysis. Protein levels were quantified as described above. Error bars represent SEM. The significant difference between Neg+EV and all the other samples is indicated by: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. e–f PKC kinase assays examining the effect of MIR2052HG and LMTK3 on the catalytic activity of PKC in MCF7/AC1 (e) and CAMA-1 (f) cells. Error bars represent SEM of two independent experiments in triplicate; **p < 0.01. g Effects of MIR2052HG silencing on ERα protein levels in the presence of a PKC inhibitor (Go 6983). Protein levels were quantified as described above. Error bars represent SEM. The significant difference between Neg and all the other samples is indicated by *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01