Figure 1. Mode of operation for the DMET array.
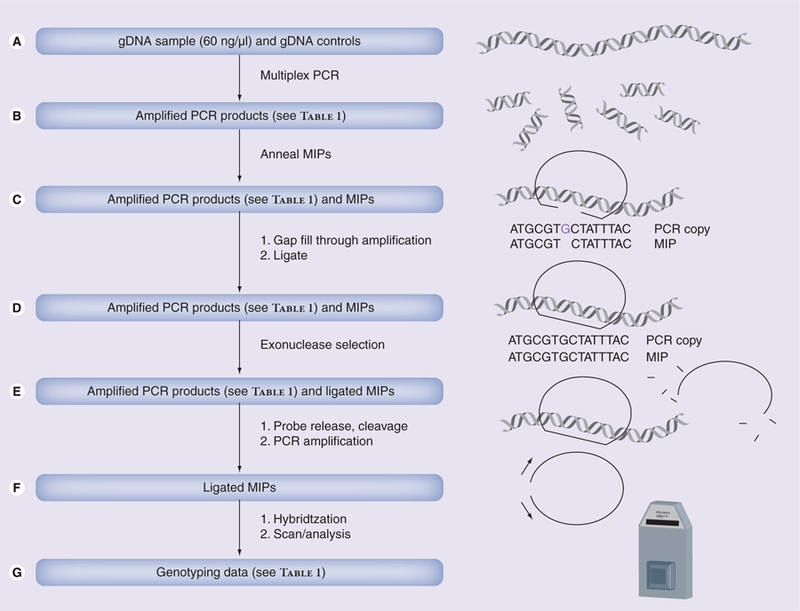
Data is generated by (A) amplifying genomic DNA (60 ng/µl) and controls at regions of interest using multiplex PCR. (B) Heat denaturing a mixture of PCR products and MIPs, and bringing the mixture to annealing temperature such that MIPs anneal at SNP sites. (C) Adding thermostable DNA polymerase, unlabeled dNTPs and ligase to extend the MIP probes and ligate them into circular form. (D) Adding exonuclease to eliminate any unligated MIPs. (E) Releasing the MIP probe from the DNA, cleaving the probes at common cleavage sites, and amplifying the remaining MIPs with labeled dNTPs. (F) Hybridizing the MIPs to the DMET array and reading the signal emitted from the labeled, hybridized MIP probes, followed by (G) interpreting the signal to generate genotyping data.
DMET: Drug Metabolizing Enzymes and Transporters; gDNA: Genomic DNA; MIP: Molecular inversion probe.
