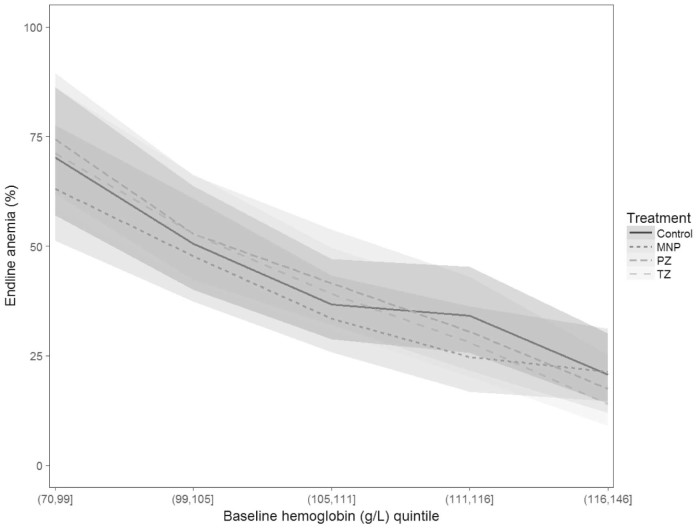
Figure 2.
Effects of 32-40 weeks of supplementation with daily preventive zinc supplements, micronutrient powder, or therapeutic zinc supplements for diarrhea on anemia prevalence among rural Laotian children, stratified by baseline hemoglobin concentrations. *Models adjusted for age, sex, district, and baseline hemoglobin. No effects of micronutrient powder on anemia in previously nonanemic children (baseline Hb ≥110; P > .05 for all pairwise comparisons); in previously anemic children (baseline Hb <110), the micronutrient powder reduced the prevalence of anemia by 9 percentage points (vs preventive zinc; P = .008), by 7 percentage points (vs therapeutic zinc; P = .041) and by 6 percentage points (vs control, P = .08). MNP, micronutrient powder; PZ, preventive zinc; TZ, therapeutic zinc.